Crucifixion - Tumblr Posts
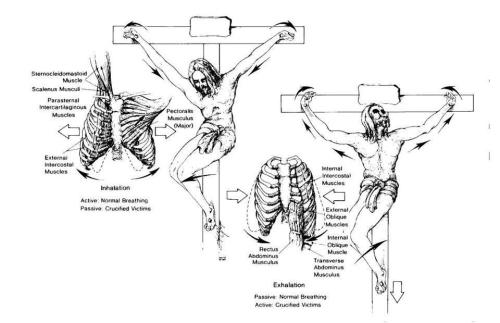
The Anatomical And Physiological Details Of Death By Crucifixion: By Dr. C. Truman Davis A Physician Analyzes the Crucifixion. From New Wine Magazine, April 1982. Originally published in Arizona Medicine, March 1965, Arizona Medical Association. Crucifixion was invented by the Persians in 300 BC, and perfected by the Romans in 100 BC. 1,It is the most painful death ever invented by man and is where we get our term “excruciating.” 2,It was reserved primarily for the most vicious of male criminals. Jesus refused the anaesthetic wine which was offered to Him by the Roman soldiers because of His promise in Matthew 26: 29, “But I say to you, I will not drink of this fruit of the vine from now on until that day when I drink it new with you in My Father’s kingdom.” 3,Jesus was stripped naked and His clothing divided by the Roman guards. This was in fulfilment of Psalm 22:18, “They divide My garments among them, and for My clothing they cast lots.” 4,The Crucifixion of Jesus guaranteed a horrific, slow, painful death. Having been nailed the Cross, Jesus now had an impossible anatomical position to maintain. 5,Jesus’ knees were flexed at about 45 degrees, and He was forced to bear His weight with the muscles of His thigh, which is not an anatomical position which is possible to maintain for more than a few minutes without severe cramp in the muscles of the thigh and calf. 6,Jesus’ weight was borne on His feet, with nails driven through them. As the strength of the muscles of Jesus’ lower limbs tired, the weight of His body had to be transferred to His wrists, His arms, and His shoulders. 7,Within a few minutes of being placed on the Cross, Jesus’ shoulders were dislocated. Minutes later Jesus’ elbows and wrists became dislocated. 8,The result of these upper limb dislocations is that His arms were 9 inches longer than normal, as clearly shown on the Shroud. 9,In addition prophecy was fulfilled in Psalm 22:14, “I am poured out like water, and all My bones are out of joint.” 10,After Jesus’ wrists, elbows, and shoulders were dislocated, the weight of His body on his upper limbs caused traction forces on the Pectoralis Major muscles of His chest wall. 11,These traction forces caused His rib cage to be pulled upwards and outwards, in a most unnatural state. His chest wall was permanently in a position of maximal respiratory inspiration. In order to exhale, Jesus was physiologically required to force His body. 12,In order to breathe out, Jesus had to push down on the nails in His feet to raise His body, and allow His rib cage to move downwards and inwards to expire air from His lungs. 13,His lungs were in a resting position of constant maximum inspiration. Crucifixion is a medical catastrophe. 14,The problem was that Jesus could not easily push down on the nails in His feet because the muscles of His legs, bent at 45 degrees, were extremely fatigued, in severe cramp, and in an anatomically compromised position. 15,Unlike all Hollywood movies about the Crucifixion, the victim was extremely active. The crucified victim was physiologically forced to move up and down the cross, a distance of about 12 inches, in order to breathe. 16,The process of respiration caused excruciating pain, mixed with the absolute terror of asphyxiation. 17,As the six hours of the Crucifixion wore on, Jesus was less and less able to bear His weight on His legs, as His thigh and calf muscles became increasingly exhausted. There was increasing dislocation of His wrists, elbows and shoulders, and further elevation of His chest wall, making His breathing more and more difficult Within minutes of crucifixion Jesus became severely dyspnoeic (short of breath). 18,His movements up and down the Cross to breathe caused excruciating pain in His wrist, His feet, and His dislocated elbows and shoulders. 19,The movements became less frequent as Jesus became increasingly exhausted, but the terror of imminent death by asphyxiation forced Him to continue in His efforts to breathe. 20,Jesus’ lower limb muscles developed excruciating cramp from the effort of pushing down on His legs, to raise His body, so that He could breathe out, in their anatomically compromised position. 21,The pain from His two shattered median nerves in His wrists exploded with every movement. 22,Jesus was covered in blood and sweat. 23,The blood was a result of the Scourging that nearly killed Him, and the sweat as a result of His violent involuntary attempts to effort to expire air from His lungs. Throughout all this He was completely naked, and the leaders of the Jews, the crowds, and the thieves on both sides of Him were jeering, swearing and laughing at Him. In addition, Jesus’ own mother was watching. 24,Physiologically, Jesus’ body was undergoing a series of catastrophic and terminal events. 25,Because Jesus could not maintain adequate ventilation of His lungs, He was now in a state of hypoventilation (inadequate ventilation). 26,His blood oxygen level began to fall, and He developed Hypoxia (low blood oxygen). In addition, because of His restricted respiratory movements, His blood carbon dioxide (CO2) level began to rise, a condition known as Hypercapnia. 27,This rising CO2 level stimulated His heart to beat faster in order to increase the delivery of oxygen, and the removal of CO2 28,The Respiratory Centre in Jesus’ brain sent urgent messages to his lungs to breathe faster, and Jesus began to pant. 29,Jesus’ physiological reflexes demanded that He took deeper breaths, and He involuntarily moved up and down the Cross much faster, despite the excruciating pain. The agonising movements spontaneously started several times a minute, to the delight of the crowd who jeered Him, the Roman soldiers, and the Sanhedrin. 30,However, due to the nailing of Jesus to the Cross and His increasing exhaustion, He was unable to provide more oxygen to His oxygen starved body. 31,The twin forces of Hypoxia (too little oxygen) and Hypercapnia (too much CO2) caused His heart to beat faster and faster, and Jesus developed Tachycardia. 32,Jesus’ heart beat faster and faster, and His pulse rate was probably about 220 beats/ minute, the maximum normally sustainable. 33,Jesus had drunk nothing for 15 hours, since 6 pm the previous evening. Jesus had endured a scourging which nearly killed Him. 34,He was bleeding from all over His body following the Scourging, the crown of thorns, the nails in His wrists and feet, and the lacerations following His beatings and falls. 35,Jesus was already very dehydrated, and His blood pressure fell alarmingly. 36,His blood pressure was probably about 80/50. 37,He was in First Degree Shock, with Hypovolaemia (low blood volume), Tachycardia (excessively fast Heart Rate), Tachypnoea (excessively fast Respiratory Rate), and Hyperhidrosis (excessive sweating). 38,By about noon Jesus’ heart probably began to fail. 39,Jesus’ lungs probably began to fill up with Pulmonary Oedema. 40,This only served to exacerbate His breathing, which was already severely compromised. 41,Jesus was in Heart Failure and Respiratory Failure. 42,Jesus said, “I thirst” because His body was crying out for fluids. 43,Jesus was in desperate need of an intravenous infusion of blood and plasma to save His life 44,Jesus could not breathe properly and was slowly suffocating to death. 45,At this stage Jesus probably developed a Haemopericardium. 46,Plasma and blood gathered in the space around His heart, called the Pericardium. 47,This fluid around His heart caused Cardiac Tamponade (fluid around His heart, which prevented Jesus’ heart from beating properly). 48,Because of the increasing physiological demands on Jesus’ heart, and the advanced state of Haemopericardium, Jesus probably eventually sustained Cardiac Rupture. His heart literally burst. This was probably the cause of His death. 49,To slow the process of death the soldiers put a small wooden seat on the Cross, which would allow Jesus the “privilege” of bearing His weight on his sacrum. 50,The effect of this was that it could take up to nine days to die on a Cross. 51,When the Romans wanted to expedite death they would simply break the legs of the victim, causing the victim to suffocate in a matter of minutes. This was called Crucifragrum. 52,At three o'clock in the afternoon Jesus said, “Tetelastai,” meaning, “It is finished.” At that moment, He gave up His Spirit, and He died. 53,When the soldiers came to Jesus to break His legs, He was already dead. Not a bone of His body was broken, in fulfilment of prophecy (above). 54,Jesus died after six hours of the most excruciating and terrifying torture ever invented. 55,Jesus died so that ordinary people like you and me could go to Heaven. All He Asks You is to Love Him, Your Lord, Your God with all your heart and with all your soul and with all your strength and with all your mind’!!
Christ's Atonement and the Rapture Found in the Dead Sea Scrolls
By Goodreads Author Eli of Kittim
The extant texts found at Qumran in the 1940s and '50s bear further revelations in regard to the coming of a rejected Messiah. As we reexamine these timeless manuscripts, we will focus our attention exclusively on the so-called 4Q541 Fragment. This text contains many eschatological themes often found in the New Testament, such as the rejection and suffering of a messianic figure, his atonement for the people of his generation, the rapture of the faithful, a thematic equivalent to the wrath of the Lamb, the end of all evil, and possibly the Messiah’s resurrection from the dead. The translation is derived from The Dead Sea Scrolls Uncovered by Robert H. Eisenman and Michael Owen Wise (1992, Element Books).
Based on the linguistic and thematic material, the context of the 4Q541 Fragment is indisputably eschatological, that is to say, concerned with the final events of human history. We should also point out that there is a thematic consistency with regard to the use of the pronoun "he," which is scattered throughout the text, so that the identity of this person remains uniform. So, let's examine the text. In column 4, fragment 3, it is said that “The fire shall be kindled in all the corners of the earth." As a textual comparison, the Bible says: “But the day of the Lord will come like a thief. The heavens will disappear with a roar; the elements will be destroyed by fire, and the earth and everything done in it will be laid bare" (2 Peter 3:10). Column 4, fragment 3 reads: "Upon the darkness it will shine," meaning the "light" of God. It is reminiscent of John 1:5, which refers to the coming of the Messiah, Jesus Christ, as the light of God: "The light shines in the darkness, and the darkness has not overcome it." In fact, in Column 4, fragments 3 and 4 seem to suggest that the timeline of this event is set for the end of human history, when all evil will be banished from the earth: “Upon the Darkness it will shine. Then the Darkness will pass away (4) [from] the earth and the deep Darkness from the dry land." This future time period, characterized by peace on earth, is mentioned numerous times in the Bible. The prophet Isaiah refers to it thusly:
"They will beat their swords into plowshares and their spears into pruning hooks. Nation will not take up sword against nation, nor will they train for war anymore" (2:4).
The idea that "the darkness will pass away (4) [from] the earth" at the end of days, and not before, is particularly evident in another Dead Sea Scroll, to wit, the famous War Scroll, otherwise known as 1QM. This text references a great battle that will ensue between the forces of light and those of darkness at the final point of time.
Another indication that the 4Q541 Fragment is referring to the so-called "last days" can be found in Column 5, Fragment 1. This fragment is obviously referring to the "sons" of God, and explicitly mentions that "(3) Some of his sons shall walk... (4) They shall be gathered to the Heav[enly Beings]..." The thematic and linguistic correspondence between this fragment and certain New Testament passages regarding the "rapture" of the faithful is unmistakable! By comparison, the New Testament uses the exact same word "gathered" to suggest the "rapture" (i.e., the ascension of physical beings into heaven): “Concerning the coming of our Lord Jesus Christ and our being gathered to him ..." (2 Thess. 2:1). The notion of the rapture, as illustrated in the 4Q541 Fragment, is virtually identical in the New Testament text:
"We who are still alive and are left will be caught up together with them in the clouds to meet the Lord in the air. And so we will be with the Lord forever" (1 Thess. 4:17).
Thus, physical beings "shall be gathered to the Heav[enly Beings ]..." This idea is echoed in the New Testament:
"In a flash, in the twinkling of an eye, at the last trumpet. For the trumpet will sound, the dead will be raised imperishable, and we will be changed. For the perishable must clothe itself with the imperishable, and the mortal with immortality" (1 Cor. 15:52-53).
However, if in fact the 4Q541 Fragment is referring to the "eschaton" (i.e., the end of human history), does it have anything to say concerning the timeline of the Messiah? The answer is, yes! The context and content of Column 4 are obviously related to the rest of the 4Q541 thematic material, and therefore suggest that the referenced messianic figure is contemporaneous with the "generation" of those who "shall be gathered to the Heav[enly Beings]..." In that regard, Column 4 expounds on the idea of a rejected messianic figure who will make an atonement (i.e., a "sacrifice") for all the people of his generation. However, mention is made that "He will overthrow his evil generation" and that "there will be [great wrath]." This is reminiscent of "the wrath of the Lamb" at the end of days, referenced in the book of Revelation:
"They called to the mountains and the rocks, 'Fall on us and hide us from the face of him who sits on the throne and from the wrath of the Lamb!'" (6:16).
Column 4 goes on to say that "When he arises ... the people will ... be confounded." The question is, where does he arise from? The text is unclear, but given that there is a glaring thematic correspondence between the eschatological content and context of the 4Q541 text and that of the Bible, it seems fairly obvious that it is not referring to anything other than a resurrection! Compare Isaiah 2:19:
"Men will go into caves of the rocks And into holes of the ground Before the terror of the LORD And the splendor of His majesty, When He arises to make the earth tremble."
Another biblical translation renders it thusly: “when he rises to terrify the earth" (ESV). This is a conspicuous allusion to the Messiah, whose resurrection signifies the end of all evil and the commencement of Judgment. Let's read what Column 4 actually says:
"(1)... his Wisdom [will be great.] He will make atonement for all the children of his generation. He will be sent to all the sons of (2) his [generation]. His word shall be as the word of Heaven and his teaching shall be according to the will of God. His eternal sun shall burn brilliantly. (3) The fire shall be kindled in all the corners of the earth. Upon the Darkness it will shine. Then the Darkness will pass away (4) [from] the earth and the deep Darkness from the dry land. They will speak many words against him. There will be many (5) [lie]s. They will invent stories about him. They will say shameful things about him. He will overthrow his evil generation (6) and there will be [great wrath]. When he arises there will be Lying and violence, and the people will wander astray [in] his days and be confounded."
There are also other literary considerations concerning the 4Q541 text that were not addressed, such as its thematic correspondence to the portrait of Jesus in the gospels, as can be readily seen in the reference to one who is guiltless, but who nevertheless undergoes scourging and affliction. Column 5 (Fragment 5) says: "(1)... and those who are grieved concerning... (2) your ju[dgment] but you will not be gui[lty]... (3) the scourging of those who afflict you... (4) your complaint (?) will not fail and all... (5) your heart be[fore]... " Mention is also made of a crucifixion, and a "nail," which are arguably literary references to the crucifixion of Jesus. Column 6 reads:
"(1) God [will set] right error[s]... [He will judge] revealed sins... (2) Investigate and seek and know how Jonah wept. Thus, you shall not destroy the weak by wasting away or by [crucif]ixion... . (3) Let not the nail touch him. Then you shall raise up for your father a name of rejoicing and for all of your brothers a [firm] Foundation. (4)... You shall see and you shall rejoice in the Eternal Light and you will not be one who is hated (of God)."
In summary, the 4Q541 Fragment, like the War Scroll, seems to contain a prophecy of the end of days. Similar to Isaiah Chapter 53, the central theme centers around the idea of a rejected and suffering messianic figure whose teaching will come from heaven, and "according to the will of God. His eternal sun shall burn brilliantly" (Column 4, fragment 2). Within an eschatological context, it is said that he will make an atonement for all the people of his generation. By comparison, the New Testament says that Jesus will sacrifice himself for humanity's sins "Once in the end of the world": “Once in the end of the world hath he appeared to put away sin by the sacrifice of himself" (Hebrews 9:26). In addition, the 4Q541 text refers to an end time period when this messianic figure will arise (presumably from the dead), and unleash his wrath, thereby putting an end to all evil in the world. It also mentions that mortals will be transported to heaven (i.e., "rapture").
In the final analysis, the messianic thematic correspondence between the 4Q541 Fragment and the New Testament is undeniable! What is more, according to the 4Q541 text, the timeline regarding the coming of this Messiah is set for the end of days, when all of this world's darkness will be obliterated, and all evil overthrown.


The Quran’s Alternative Christianity
By Goodreads Author Eli Kittim
——-
Christianity’s Influence on the Quran
Although polytheism was the dominant form of religion in pre-Islamic Arabia, the Quran was diametrically opposed to this view and superseded it with its own brand of monotheism. The unknown author(s) of the Quran was obviously influenced by the Gnostic religion of the Mandaeans, who are sometimes called "Christians of Saint John," and by that of the Sabians or Manichaeans, who revered certain prophets, such as Zoroaster and Jesus. Despite these strong surrounding influences, however, the author(s) of the Quran seems to gravitate towards the Judeo-Christian Bible, paying special attention to the Jesus story and accepting even some of its more miraculous or fantastic elements, such as the virgin birth and the 2nd coming. That’s a clue that Christianity made a greater impact on the author(s) of the Quran than, say, Mithraism, Zoroastrianism, or Mazdakism! If, on the other hand, the author(s) of the Quran had used Judaism as a prototype of his new religion, then, in principle, he would never have accepted the Christian claims. Besides, Islam doesn’t show strict adherence to circumcision or the Law. And even though Moses and Abraham are mentioned more times than Jesus in the Quran, it’s rather obvious that Christianity had made a deeper impact on the author(s) than any other religion! And just as Christianity accepted the Hebrew Bible, so did the Quran.
——-
A Christian Revolt
Do you really know what the Quran is? Answer: the product of a late *Gnostic Christian revolt* against Byzantine Orthodoxy. No wonder its adherents hated Constantinople so vigorously that they finally sacked it in 1453 ce. What I am proposing is that the *Gnostic-Christian Sects* that were marginalized by Byzantine Orthodoxy from the fourth century onwards didn’t go away quietly but seemingly conspired against the Church during the early part of the dark ages! The result of those efforts eventuated in the Book we now call the Quran. The syncretistic-gnostic elements present in the Quran suggest that it was in fact an amalgamation of heresies that characterized many different Gnostic Christian sects.
——-
The Apocryphal Reformation
After the 4th-Century Church solidified itself theologically and otherwise within the Roman Empire and began to accept certain “canonical” texts while excluding others, those communities that held to the *rejected* gnostic and so-called “apocryphal” works eventually united to form their own Bible. The result was the Quran, which was mostly based on a variety of Jewish and Christian apocryphal and Gnostic texts!
Over time, Islam gradually lost it’s connection to Christianity (much like Christianity did when it broke away from Judaism) and became an independent religion in its own right. It may have been more Christ-centered at the beginning. But in order to distinguish itself from its rival Christian counterparts it would have had to significantly deemphasize its central Christian tenets. So, the first communities that gave rise to the Quran most probably comprised Gnostic Christians. Thus, the author of the Quran may have been seeking to take revenge on his Orthodox superiors, much like what a disgruntled Christian priest would do at a local church. Martin Luther immediately comes to mind and, with him, the Protestant Reformation!
——-
The Beginning of Islam as a Christian Minority Religion
No wonder the Quran reveres the Christian dogmas of the virgin birth and the second coming of Jesus, while putting less emphasis on the historical Jesus, his atonement, and his divinity! And the Islamic traditions begin to make more sense from this perspective, as, for example, when the Nestorian monk Bahira in Bosra foretold to the adolescent Muhammad his future prophetic career. And just as Orthodoxy condemned the Gnostic Christian texts as *heretical* and *uninspired*, Islam must have fired back at them alleging that the so-called “canonical Christian texts” themselves were *corrupt*. It seems, then, that Islam itself came out of these early Gnostic-Nestorian Christian roots! In other words, even though it now openly competes with Christianity for converts, originally, Islam must have been a Christian minority religion on the fringes of the Eastern Roman Empire that was well-aware of all the debates that were raging all around them.
——-
The New Testament Epistles Concur with the Apocryphal Texts that Undergird the Quran
As an offshoot of Christian Gnosticism, with an emphasis on personal existential experience rather than reason or doctrine, the Quran was, perhaps, closer to the truth than the pontifical, dogmatic Christianity of the Roman Empire. Gnosis, after all, was all about knowing rather than believing. And just because the Gnostic Christian texts were rejected by the church does not necessarily mean that they were wholly uninspired. For example, the Second Treatise of the Great Seth and the Gnostic Apocalypse of Peter, as attested in the Quran (Sura 4:157-158), doubt the established Crucifixion story and, by implication, perhaps even Jesus’ historicity. In other words, the Quran picked up Docetic thoughts and Gnostic ideas and asserted that all the acts and sufferings of Jesus’ life, including the crucifixion, were mere appearances. This is a noteworthy observation because, unlike the theological gospels, the New Testament epistles also suggest that Christ did not die in antiquity. Rather, they claim that he will be revealed “at the final point of time” (1 Pet. 1.20 NJB) and will die “once in the end of the world” (Heb. 9.26b). This idea of an earthly, eschatological messiah is also echoed in the pseudepigraphical Jewish-Christian texts, The Ascension of Isaiah and the Testament of Solomon. But it had been subsequently suppressed by Orthodox Christianity, which confused theology with history, and turned prophecy into biography. So, in this sense, Islam was correct in maintaining that the New Testament had been corrupted: not the text itself, but rather it’s interpretation.
However, as time passed, and as Islam separated itself more and more from Christianity, it, too, began to lose touch with the central tenet of Christ’s divinity, while its adherents took too many liberties with the original doctrines and became less and less “Christian”! To the extent that Islam gravitated away from Christ as the focal point of its doctrines, it, too, became corrupt, so much so that the deity of Christ was completely ignored or denied. Eventually, the religion’s deity became more identified with the monotheistic God of the Jews than with that of the Christians. That was the beginning of something new: the birth of a new religion!
——-
Family Feud Among the Abrahamic Religions
To sum up, Judaism, Christianity, and Islam are all part of the family of Abraham. Hence why they are called Abrahamic religions. Christianity, which grew out of Judaism, in turn, gave birth to Islam! But in the end, it’s like a dysfunctional family where the grandfather, father, and son can’t get along with each other.
——-
Atrayo's Oracle Vlog on the Three Mercies of Christ's Crucifixion
I'm the Clairvoyant author as a sage and angelic mystic to the channeled angelic spiritual wisdom book series of "Jewels of Truth" Volume 1, 2, and 3. I'm a visionary futurist as an Inspirational muse focusing on innovative original conceptual designs as potential solutions as a form of dharmic service.
Today's "Jewels of Truth" statement 1,751 seems to have written itself in 2 parts. One of the origins of Creation and another on the passing of a Great Prophet, if not Savior to many more as "Jesus the Christos". As angelically channeled spiritual wisdom content for all regardless of faith in this world.
Jewels of Truth website: http://jewelsoftruth.us
Atrayo's Oracle Blog Link for July 7th, 2014

“Heart Crucifixion”. Álvaro Barcala, October 2020
From my series of drawings “Wonderful Blood”
The gaze of Jesus upon the Cross penetrates to the depths of our soul and touches it with repentance, because we are made to understand that sin is the cause of all these sufferings.
Dom Marmion - Christ, the Ideal of the Monk, p. 170

