Christian Apologetics - Tumblr Posts
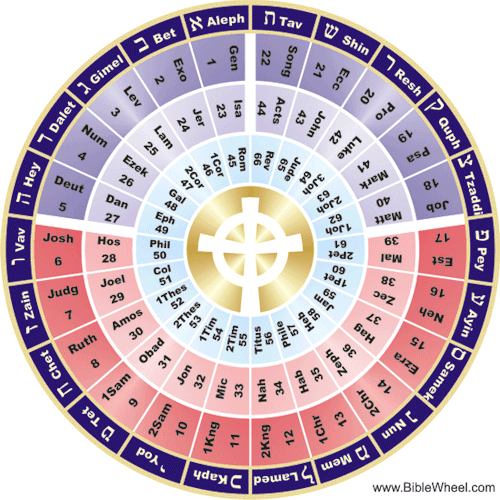
A Critical Review of the So-Called “Bible-Wheel” method of Biblical Interpretation
By Author Eli Kittim
——-
Like the Zohar in the Kabbalah, the “Bible-Wheel” approach is a kind of Hebraic “Gematria” or “Isopsephy” that corresponds to the letters of the Hebrew alphabet but does not take into consideration several important Biblical factors. For instance, it doesn’t consider the fact that the New Testament uses a different alphabet (i.e. Greek), nor does it seriously consider the historical-grammatical context of the New Testament books. The Bible Wheel’s premise is that “the Hebrew alphabet is established in the alphabetically structured passages of the Old Testament, most notably Psalm 119 that praises God's Word from Aleph to Tav, from beginning to end.” This “is a circular presentation of the Bible . . . by rolling up the traditional list of the sixty-six books like a scroll on a spindle wheel of twenty-two spokes.” Here’s how it works:
“The structure consists of a circular matrix of sixty-six Cells on a Wheel of twenty-two Spokes. The sixty-six Cells form three wheels within the Wheel called Cycles. Each Cycle spans a continuous sequence of twenty-two books as follows: With the completion of the Bible Wheel, we now have a fully unified view of the whole Bible as a symmetrical, mathematically structured two-dimensional object. The increase from the traditional one-dimensional list of books to the two-dimensional Bible Wheel immediately reveals a host of unanticipated correlations between the three books on each spoke with each other and the corresponding Hebrew Letter” (according to biblewheel.com).
This is more of an “intuitive” rather than a scholarly approach to the Bible that is devoid of historical, grammatical, hermeneutical, and contextual considerations. For example, the premise that the entire Biblical structure of the 66 canonical books is grounded exclusively in the Hebrew alphabet “from Aleph to Tav, from beginning to end” is debunked by Christ’s self-disclosure and promulgation of the Divine Name explicitly through the Greek alphabet:
ἐγὼ τὸ Ἄλφα καὶ τὸ Ὦ, ὁ πρῶτος καὶ ὁ ἔσχατος, ἡ ἀρχὴ καὶ τὸ τέλος (SBLGNT).
Translation:
“I am the Alpha and the Omega, the First and the Last, the Beginning and the End” (Rev. 22.13 NRSV).
There is absolutely no correlation, here, to the Aleph and Tav or to the Hebrew alphabet. On the contrary, Christ reveals the divine name in the language of the Greeks by declaring “I am the Alpha and the Omega, the First and the Last, the Beginning and the End.” The alpha and omega are the first and last letters of the Greek writing system, that is to say, the beginning and the end of the Greek alphabet!
What is more, the Bible wheel practice is based not on scholarly criteria (i.e. detailed exegesis/authorial intent) but rather on apparent coincidences (e.g. mathematical, alphabetic, Hebraic, etc.), sometimes explained through a matrix that we might call “synchronicity”:
//Synchronicity is a concept, first introduced by analytical psychologist Carl Jung, which holds that events are "meaningful coincidences" if they occur with no causal relationship yet seem to be meaningfully related. During his career, Jung furnished several different definitions of the term, defining synchronicity as an "acausal connecting (togetherness) principle;" "meaningful coincidence;" "acausal parallelism;” and as a "meaningful coincidence of two or more events where something other than the probability of chance is involved.// (Wiki).
Therefore, although it may have some symbolic preliminary merits, the Bible wheel practice is obviously not a credible or scholarly approach to Biblical investigation.
The notion that the 66 Books of the Bible can be put on an apparent wheel where each book directly coincides with some other book based on certain numerical, alphabetical, and Hebraic correlations seems to be an outlandish explanation! This practice, including its pictorial representation, is somewhat reminiscent of the medieval divination practices of occultism, such as Kabbalah, Cartomancy (i.e. Tarot card reading) and Numerology:
“Numerology is any belief in the divine or mystical relationship between a number and one or more coinciding events. It is also the study of the numerical value of the letters in words, names, and ideas. It is often associated with the paranormal, alongside astrology and similar divinatory arts” (Wiki).
——-
The idea behind the Bible-Wheel approach is that Biblical history repeats itself: that time is cyclical. What is the axiom of this interpretive method? As It Was, So Shall It Be… It, therefore, presupposes that there are thematic parallels (and secret codes) between the earlier books of the Bible and the later ones. Similar methods have been proposed by authors Perry Stone and Jonathan Cahn. Thus, with the exception of some trivial and peripheral similarities, I don’t see any major thematic affinities, say, between Jeremiah 17 and Revelation 2, as per the Bible-wheel interpretation.
——-
Let’s Look at Rev. 2
——-
The Church of Ephesus has a lot going for it. It endures with patience, does not tolerate evil, exposes falsehood, and bears much for the sake of Christ (Rev. 2.2-3). No such praise is ever mentioned in Jer. 17 in relation to to the Jews. Furthermore, despite some set backs, God promises certain divine rewards in Rev. 2 that are not mentioned in Jer. 17, namely, offering the faithful the crown of life (Rev. 2.10) as well as eternal life: “Whoever conquers will not be harmed by the second death” (Rev. 2.11), etc.
——-
Similarly, the Church of Pergamum, despite its shortcomings, is holding fast. Even though it’s located within Satan’s domain, so to speak, it’s holding on to Christ and has not denied the faith (Rev. 2.13).
Here, as before, Christ offers the divine manna and a mystic precious stone to the over-comers (Rev. 2.17). Nothing of the kind is ever referenced in Jer. 17.
——-
Also, the Church in Thyatira is not doing too bad either. Christ is aware of its works—such as “love, faith, service, and patient endurance” (Rev. 2.19). And although some have incorporated certain false teachings, there are others within the church that are blameless and whom Christ does not rebuke at all (Rev. 2.24)! He simply urges them to hold on til he comes (Rev. 2.25). Christ maintains that anyone who endures to the end will be granted “authority over the nations” (v. 26) and will also receive “the morning star” (v.28).
——-
Now Let’s Look at Jer. 17
——-
By contrast, Jeremiah 17 is casting an aspersion on the kingdom of Judah. Its proemium is as follows:
“The sin of Judah is written with an iron pen; with a diamond point it is engraved on the tablet of their hearts, and on the horns of their altars” (Jer. 17.1 NRSV).
Next, there are a number of caveats that culminate in God’s vow to eternally disinherit the Jews from his promises:
“By your own act you shall lose the heritage that I gave you, and I will make you serve your enemies in a land that you do not know, for in my anger a fire is kindled that shall burn forever” (v. 4). Then God recites a summary of the Blessings and Curses of the covenant (vv. 5-9). Finally, Jeremiah exalts the Lord and offers up his own defense that he is upright, and so on. Here, the text instructs the people of Judah to keep certain commandments, such as “the sabbath day” (v. 24), something that does not occur in Rev. 2. The chapter ends with Blessings and Curses in the form of rewards and punishments (vv. 26-27).
Incidentally, the theme of God who “searches minds and hearts,” in Rev. 2.23, is a common trope that can be found in various places in the Bible and is not exclusive to Jeremiah 17.10 (e.g., 1 Ch. 28.9; 29.17; Ps. 7.9; Prov. 17.3; Ecc. 3.18; Jer. 11.20; Rom. 8.27), as proponents of this view suggest.
——-
Conclusion
Unlike Rev. 2, nowhere is there any mention of eternal life or of surviving a second death in Jer. 17. Moreover, no one is offered any rewards of authority over nations, or any glory, for that matter, such as that implied by the so-called “morning star.” In fact, there’s no one blameless in Jer. 17, nor does any praise come from God concerning anyone whatsoever. Even the prophet himself has to plead for mercy and proclaim his own self-righteousness. Besides, there are so many other differences.
Jeremiah is written in *Hebrew* and heavily redacted probably by the scribe Baruch and later generations of Deuteronomists, while Revelation is written exclusively in *Greek* most likely by a single author. The former is probably from the 6th century BCE, while the latter dates from ca. 95 CE. One is written to a Jewish nation, the kingdom of Judah, just prior to the Babylonian deportation, while the other is written to the predominantly Gentile Churches in Asia Minor. One is written in Palestine, the other in Greece! So where are the parallels?
——-

How Can Good Exegesis Make Bad Theology?
By Author Eli Kittim
——-
The Canonical Context
This principle suggests that we should read the Books of the Bible not as distinct, individual compositions but rather as parts of a larger *canonical context*, that is, as part of the “canon” of Scripture. In other words, instead of evaluating each book separately in terms of its particular historical, literary, and editorial development, this principle focuses instead on its final canonical format that was legitimized by the various communities of faith. The idea is that since the redacted version or “final cut,” as it were, is considered “authoritative” by the different communities of faith, then this format should hold precedence over all previous versions or drafts.
Moreover, this concept holds that despite the fact that the Biblical Books were written by a number of different authors, at different times, in different places, using different languages, nevertheless the “canonical context” emphasizes the need to read these Books in dialogue with one another, as if they are part of a larger whole. So, the hermeneutical focus is not on the historical but rather on the canonical context. The hermeneutical guidelines of the canon therefore suggest that we might gain a better understanding of the larger message of Scripture by reading these Books as if they were interrelated with all the others, rather than as separate, diverse, and distinct sources. The premise is that the use of this type of context leads to sound Biblical theology.
——-
Theology
Theology is primarily concerned with the synthesis of the diverse voices within Scripture in order to grasp the overarching message of the complete Biblical revelation. It deals with Biblical epistemology and belief, either through systematic analysis and development of passages (systematic theology) or through the running themes of the entire Bible (Biblical theology). It addresses eternity and the transcendent, metaphysical or supernatural world. And it balances individual Scriptural interpretations by placing them within a larger theoretical framework. The premise is that there is a broader theological context in which each and every detailed exegesis coalesces to form a coherent whole! It’s as if the Bible is a single Book that contains a complete and wide-ranging revelation! It is under the auspices of theology, then, that the canonical context comes into play.
——-
Exegesis
The critical interpretation of Scriptural texts is known as “exegesis.” Its task is to use various methods of interpretation so as to arrive at a definitive explanation of Scripture! Exegesis provides the temporal, linguistic, grammatical, and syntactic context, analysis, and meaning of a text. It furnishes us with a critical understanding of the authorial intent, but only in relation to the specific and limited context of the particular text in question. It is the task of theology to further assess it in terms of its relation and compatibility to the overall Biblical revelation! One of the things that exegesis tries to establish is the composition’s historical setting or context, also known as “historical criticism.” This approach inquires about the author and his audience, the occasion and dating of the composition, the unique terms and concepts therein, the meaning of the overall message, and, last but not least, the *style* in which the message is written, otherwise known as the “genre.” While the author’s other writings on the topic are pivotal to understanding what he means, nothing is more important than the *genre* or the form in which his writing is presented.
——-
The Analogy of Scripture
One of the most important hermeneutical principles of exegesis is called “the analogy of Scripture” (Lat. ‘analogia Scripturae’). In short, it means that Scripture should interpret Scripture. This principle requires that the implicit must be explained by the explicit. In other words, the exegesis of unclear or ambiguous parts of Scripture must be explained by clear and didactic ones that address the exact same topic. That means that one Biblical Book could very well explain another. For example, the New Testament (NT) Book of Ephesians 1.9-10 seems to demystify Galatians 4.4. This principle is based on the “revealed” inspiration (Gk. θεόπνευστος) of Scripture:
All scripture is inspired by God and is useful
for teaching, for reproof, for correction, and
for training in righteousness (2 Tim. 3.16
NRSV).
As for those scholars who refuse to take the NT’s alleged “pseudepigrapha” seriously because of their *apparent* false attribution, let me remind them that the most renowned textual scholars of the 20th century, Bruce M. Metzger and Bart D. Ehrman, acknowledged that even alleged “forged” works could still be “inspired!” It’s important to realize that just because these works may be written by unknown authors who may have attempted to gain a readership by tacking on the name of famous Biblical characters doesn’t mean that the subject-matter is equally false. The addition of amanuenses (secretaries) further complicates the issue.
So, returning to our subject, the analogy of Scripture allows the Bible to define its own terms, symbols, and phrases. It is via the analogy of Scripture, which defines the many and varied parts, that the broader canonical context is established, namely, the principle that the various Biblical Books form a coherent whole from which a larger theological system can emerge.
And, of course, interdisciplinary studies——such as archaeology, anthropology, psychology, sociology, epistemology, and philosophy——contribute to both systematic and Biblical theology by presenting their particular findings, concepts, and theoretical ideas.
——-
Testing the Legitimacy of these Principles
In explaining how these principles work in tandem, I’d like to put my personal and unique theology to the test. I have raised the following question: “What if the crucifixion of Christ is a future event?” The immediate reaction of Christian apologetics or heresiology would be to revert to “dogmatic theology” (i.e., the dogmas or articles of faith) and the scholarly consensus, which state that Jesus of Nazareth was crucified under Pontius Pilate during the reign of Tiberius. Really? Let’s consider some historical facts. There are no eyewitnesses! And there are no first-hand accounts! Although the following references were once thought to be multiple attestations or proofs of Jesus’ existence, nevertheless both the Tacitus and Josephus accounts are now considered to be either complete or partial forgeries, and therefore do not shed any light on Jesus’ historicity. One of the staunch proponents of the historical Jesus position is the textual scholar Bart Ehrman, who, surprisingly, said this on his blog:
. . . Paul says almost *NOTHING* about the
events of Jesus’ lifetime. That seems weird
to people, but just read all of his letters.,
Paul never mentions Jesus healing anyone,
casting out a demon, doing any other
miracle, arguing with Pharisees or other
leaders, teaching the multitudes, even
speaking a parable, being baptized, being
transfigured, going to Jerusalem, being
arrested, put on trial, found guilty of
blasphemy, appearing before Pontius Pilate
on charges of calling himself the King of the
Jews, being flogged, etc. etc. etc. It’s a
very, very long list of what he doesn’t tell us
about.
Therefore, there appears to be a literary discrepancy regarding the historicity of Jesus in the canonical context between the gospels and the epistles. And, as I will show in due time, there are many, many passages in the epistles that seem to contradict dogmatic theology’s belief in the historiographical nature of the gospels. So, if they want to have a sound theology, exegetes should give equal attention to the epistles. Why?
First, the epistles precede the gospels by several decades. In fact, they comprise the earliest recorded writings of the NT that circulated among the Christian churches (cf. Col. 4.16).
Second, unlike the gospels——which are essentially *theological* narratives that are largely borrowed from the Old Testament (OT)——the epistles are *expositional* writings that offer real, didactic and practical solutions and discuss spiritual principles and applications within an actual, historical, or eschatological context.
Third, according to Biblical scholarship, the gospels are not historiographical accounts or biographies, even though historical places and figures are sometimes mentioned. That is to say, the gospels are not giving us history proper. For example, the feeding of the 5,000 is a narrative that is borrowed from 2 Kings 4.40-44. The parallels and verbal agreements are virtually identical. And this is a typical example of the rest of the narratives. For instance, when Jesus speaks of the damned and says that “their worm never dies, and the fire is never quenched” (Mark 9.48), few people know that this saying is actually derived from Isaiah 66.24. In other words, the gospels demonstrate a literary dependence on the OT that is called, “intertextuality.”
Fourth, the gospels are like watching a Broadway play. They are full of plots, subplots, theatrical devices (e.g. Aristotelian rhetoric; Homeric parallels), literary embellishments, dialogues, characters, and the like. Conversely, the epistles have none of these elements. They are straightforward and matter of fact. That’s why Biblical interpreters are expected to interpret the implicit by the explicit and the narrative by the didactic. In practical terms, the NT epistles——which are the more explicit and didactic portions of Scripture——must clarify the implicit meaning of the gospel literature. As you will see, the epistles are the primary keys to unlocking the actual timeline of Christ’s *one-and-only* visitation!
Fifth, whereas the gospels’ literary genre is mainly •theological•——that is to say, “pseudo-historical”——the genre of the epistolary literature of the NT is chiefly •expositional.• So, the question arises, which of the two genres is giving us the real deal: is it the “theological narrative” or the “expository writing”?
In order to answer this question, we first need to consider some of the differences in both genres. For example, although equally “inspired,” the gospels include certain narratives that are unanimously rejected as “unhistorical” by both Biblical scholars and historians alike. Stories like the slaughter of the innocents, the Magi, the Star of Bethlehem, and so on, are not considered to be historical. By contrast, the epistles never once mention the aforesaid stories, nor is there any mention of the Nativity, the virgin birth, the flight to Egypt, and the like. Why? Because the Epistles are NOT “theological.” They’re expository writings whose intention is to give us the “facts” as they really are!
Bottom line, the epistles give us a far more accurate picture of Jesus’ *visitation* than the gospels.
In conclusion, it appears that the gospels conceal Jesus far more effectively than they reveal him.
——-
Proof-text and Coherence Fallacies
The “proof-text fallacy” comprises the idea of putting together a number of out-of-context passages in order to validate a particular theological point that’s often disparagingly called “a private interpretation.” But, for argument’s sake, let’s turn these principles on their head. Classical Christianity typically determines heresy by assessing the latter’s overall view. If it doesn’t fit within the existing theological schema it is said to be heretical. Thus, dogmatic theology sets the theological standard against which all other theories are measured. They would argue that good exegesis doesn’t necessarily guarantee good theology, and can lead to a “coherence fallacy.” In other words, even if the exegesis of a string of proof-texts is accurate, the conclusion may not be compatible with the overall existing theology. This would be equivalent to a coherence fallacy, that is to say, the illusion of Biblical coherence.
By the same token, I can argue that traditional, historical-Jesus exegesis of certain proof-texts might be accurate but it may not fit the theology of an eschatological Christ, as we find in the epistles (e.g., Heb. 9.26b; 1 Pet. 1.20; Rev. 12.5). That would equally constitute a coherence fallacy. So, these guidelines tend to discourage independent proof-texting apart from a systematic coherency of Scripture. But what if the supposed canonical context is wrong? What if the underlying theological assumption is off? What then? So, the $64,000 question is, who can accurately determine the big picture? And who gets to decide?
For example, I think that we have confused Biblical literature with history, and turned prophecy into biography. In my view, the theological purpose of the gospels is to provide a fitting introduction to the messianic story *beforehand* so that it can be passed down from generation to generation until the time of its fulfillment. It is as though NT history is *written in advance* (cf. מַגִּ֤יד מֵֽרֵאשִׁית֙ אַחֲרִ֔ית [declaring the end from the beginning], Isa. 46.9-10; προεπηγγείλατο [promised beforehand], Rom. 1.2; προγνώσει [foreknowledge], Acts 2.22-23; προκεχειροτονημένοις [to appoint beforehand], Acts 10.40-41; ερχόμενα [things to come], Jn 16.13)!
So, if we exchange the theology of the gospels for that of the epistles we’ll find a completely different theology altogether, one in which the coherence of Scripture revolves around the *end-times*! For example, in 2 Pet. 1.16–21, all the explanations in vv. 16-18 are referring to the future. That’s why verse 19 concludes: “So we have the prophetic message more fully confirmed” (cf. 1 Pet. 1.10-11; 1 Jn 2.28).
In response, Dogmatic Theology would probably say that such a conclusion is at odds with the canonical context and that it seems to be based on autonomous proof-texting that is obviously out of touch with the broader theological teaching of Scripture. Really? So the so-called “teaching” of Scripture that Jesus died in Antiquity is a nonnegotiable, foregone conclusion? What if the basis upon which this gospel teaching rests is itself a proof-text fallacy that is out of touch with the teaching of the *epistles*? For example, there are numerous passages in the epistles that place the timeline of Jesus’ life (i.e., his birth, death, and resurrection) in *eschatological* categories (e.g., 2 Thess. 2.1-3; Heb. 1.1-2; 9.26b; 1 Pet. 1.10-11, 20; Rev. 12.5; 19.10d; 22.7). The epistolary authors deviate from the gospel writers in their understanding of the overall importance of •eschatology• in the chronology of Jesus. For them, Scripture comprises revelations and “prophetic writings” (see Rom. 16.25-26; 2 Pet. 1.19-21; Rev. 22.18-19). Therefore, according to the *epistolary literature*, Jesus is not a historical but rather an “eschatological” figure! Given that the NT epistles are part of the Biblical *canon,* their overall message holds equal value with that of the NT gospels, since they, too, are an integral part of the canonical context! To that extent, even the gospels concede that the Son of Man has not yet been revealed (see Lk. 17.30; cf. 1 Cor. 1.7; 1 Pet. 1.7)!
What is more, if the canonical context demands that we coalesce the different Biblical texts as if we’re reading a single Book, then the overall “prophetic” message of Revelation must certainly play an important role therein. The Book of Revelation places not only the timeline (12.5) but also the testimony to Jesus (19.10b) in “prophetic” categories:
I warn everyone who hears the words of the
prophecy of this book: if anyone adds to
them, God will add to that person the
plagues described in this book; if anyone
takes away from the words of the book of
this prophecy, God will take away that
person’s share in the tree of life and in the
holy city, which are described in this book
(Rev. 22.18-19 NRSV).
Incidentally, the Book of Revelation is considered to be an epistle. Thus, it represents, confirms, and validates the overarching *prophetic theme* or eschatological “theology” of the epistolary literature. That is not to say that the •theology• of the epistles stands alone and apart from that of the OT canon. Far from it! Even the *theology* of the OT confirms the earthy, end-time Messiah of the epistles (cf. Job 19.25; Isa. 2.19; Dan. 12.1-2; Zeph. 1.7-9, 15-18; Zech. 12.9-10)! As a matter of fact, mine is the *only* view that appropriately combines the end-time messianic expectations of the Jews with Christian Scripture!
Does this sound like a proof-text or coherence fallacy? If it does, it’s because you’re evaluating it from the theology of the gospels. If, on the other hand, you assess it using the theology of the epistles, it will seem to be in-context or in-sync with it. So, the theological focus and coherency of Scripture will change depending on which angle you view it from.
——-
Visions of the Resurrection
There are quite a few scholars that view the so-called resurrection of Christ not as a historical phenomenon but rather as a visionary experience. And this seems to be the theological message of the NT as well (cf. 2 Tim. 2.17-18; 2 Thess. 2.1-3). For example, Lk. 24.23 explicitly states that the women “had indeed seen a vision.” Lk. 24.31 reads: “he [Jesus] vanished from their sight.” And Lk. 24.37 admits they “thought that they were seeing a ghost.” Here are some of the statements that scholars have made about the resurrection, which do not necessarily disqualify them as believers:
The resurrection itself is not an event of
past history. All that historical criticism can
establish is that the first disciples came to
believe the resurrection (Rudolph
Bultmann, ‘The New Testament and
Mythology,’ in Kerygma and Myth: A
Theological Debate, ed. Hans Werner
Bartsch, trans. Reginald H. Fuller [London:
S.P.C.K, 1953-62], 38, 42).
When the evangelists spoke about the
resurrection of Jesus, they told stories
about apparitions or visions (John Dominic
Crossan, ‘A Long Way from Tipperary: A
Memoir’ [San Francisco:
HarperSanFransisco, 2000], 164-165).
At the heart of the Christian religion lies a
vision described in Greek by Paul as
ophehe—-“he was seen.” And Paul himself,
who claims to have witnessed an
appearance asserted repeatedly “I have
seen the Lord.” So Paul is the main source
of the thesis that a vision is the origin of the
belief in resurrection ... (Gerd Lüdemann,
‘The Resurrection of Jesus: History,
Experience, Theology.’ Translated by John
Bowden. [London: SCM, 1994], 97,
100).
It is undisputable that some of the followers
of Jesus came to think that he had been
raised from the dead, and that something
had to have happened to make them think
so. Our earliest records are consistent on
this point, and I think they provide us with
the historically reliable information in one
key aspect: the disciples’ belief in the
resurrection was based on visionary
experiences. I should stress it was visions,
and nothing else, that led to the first
disciples to believe in the resurrection (Bart
D. Ehrman, ‘How Jesus Became God: The
Exaltation of a Jewish Preacher from
Galilee’ [New York: Harper One, 2014],
183-184).
Ehrman sides with the *visionary language* that Luke, Bultmann, Crossan, and Lüdemann use. In the words of NT textual critic Kurt Aland:
It almost then appears as if Jesus were a
mere PHANTOM . . .
——-
Exegetical Application
I deliberately stay away from theology when I exegete Scripture precisely because it will taint the evidence with presuppositions, assumptions, and speculations that are not in the text. Thus, instead of focusing on the authorial intent hermeneutic, it will inevitably superimpose out-of-context meanings and create an eisegesis. All this, of course, is courtesy of confirmation bias.
So, I think one of the reasons why we’ve done so poorly in understanding, for example, the story of Jesus is because we have mixed-up exegesis with theology. When theology drives the exegesis, then the exegesis becomes blind and erroneous.
My method of exegesis is very simple. I see EXACTLY what the text *says,* EXACTLY *how* it says it. I don’t add or subtract anything, and I don’t speculate, guess, or theorize based on existing philosophies or theologies. The minute we go outside *the analogy of scripture,* that’s when we start to speculate. And that’s how we err. In short, let the Scriptures tell you what it means. Thus, the best interpretation is no interpretation at all!
——-
Conclusion
To find the truth, we must consider all the evidence objectively. Evangelicals, for instance, would be biased if they didn’t consider the academic standpoint even if, at times, it seems to be guided by liberal theology. In this way, they will be in a better position to consider objectively all the possibilities and probabilities regarding the correct interpretation of Scripture. That’s because the truth usually touches all points of view . . .
One of the exegetical stumbling blocks is our inability to view the gospels as “inspired metaphors.” Given their literary dependence on the OT, it appears as if the gospels themselves are “inspired parables.”
So, if the epistolary literature, which is both expositional and explicit, seems to contradict these so-called “theological parables,” then it becomes quite obvious that the “theology” of the gospels fails to meet scholarly and academic parameters. And, therefore, the epistolary literature must be given more serious attention and consideration!
Our exegetical shortcomings often stem from forced or anachronistic interpretations that are based on *theological speculation* and conjecture rather than on detailed exegesis. Even the Biblical translations themselves are not immune to the interpretative process, whether they be of dynamic or formal equivalence.
That’s why I have developed an exegetical system and have demonstrated the effectiveness of its approach to the study of the Biblical Christ. Accordingly, I argue that the epistles are the primary *keys* to unlocking the future timeline of Christ’s ***ONLY*** visitation! Hence, I leave you with one final rhetorical question:
What if the crucifixion of Christ is a future
event?

The Quran: Revelation or Forgery?
By Goodreads Author Eli Kittim
——-
Did Muhammad Exist?
Before we embark on a brief criticism of the Quran, it’s important to note that there is “very little biographical information” (Wiki) concerning the historicity of its founder, Muhammad:
Attempts to distinguish between the
historical elements and the unhistorical
elements of many of the reports of
Muhammad have not been very successful
(Wiki).
(see: https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Historicity_of_Muhammad#Views_of_secular_historians).

Of course, this opens up the possibility of whether or not the unknown author of the Quran invented the Muhammad tradition to bolster his credibility. In order to determine the answer to this question, it is crucial to consider the evidence of *intertextuality* in the Quran, that is to say, the literary dependence of the Quran on earlier texts and sources.
——-
How historically reliable is the Quran?
Firstly, with regard to source criticism——that is, the sources that the Quran’s message is derived from——there are some very serious issues involved. For example, there are well-known parallelisms between the Quran and the extra-biblical, non-inspired book of Talmud (e.g. Surah 5:32; cf. Sanhedrin 37a) as well as borrowing from Christian apocryphal works that were written hundreds of years after the purported events and which claim to be legitimate Christian gospels but are not. Case in point, The Infancy Gospel of Thomas:
The Infancy Gospel of Thomas is thought to
be Gnostic in origin. . . . Early Christians
regarded the Infancy Gospel of Thomas as
inauthentic and heretical. Hippolytus
identified it as a fake and a heresy in his
Refutation of All Heresies, and his
contemporary Origen referred to it in a
similar way in a homily written in the early
third century. Eusebius rejected it as a
heretical ‘fiction’ in the third book of his
fourth-century Church History, and Pope
Gelasius I included it in his list of heretical
books in the fifth century. While non-
canonical in Christianity, the Infancy Gospel
of Thomas contains many miracles and
stories of Jesus referenced in the Qur'an,
such as Jesus giving life to clay birds (Wiki).
So, the Quran clearly employs Jewish and Christian apocryphal works that were never accepted as canonical or as “inspired” either by Jews or Christians. Thus, at least some of the sources of the Quran are highly dubious.
Secondly, in 632 CE, following Muhammad’s death, the Battle of Yamama ensued where a great number of those who had supposedly retained the Quran in their memory (hafiz) actually died. How then can Muslims claim the preservation of the Quran through memory and oral transmission?
Thirdly, the New Testament is the best attested book from the ancient world as well as the most scrutinized book in history, and one which has a critical edition. By contrast, the Quran has not been critically scrutinized rigorously in the same manner, nor does it have a critical edition, nor is the manuscript evidence made available to scholars for serious study. There’s a secrecy surrounding it that seems to prevent scholarly investigations. For example, because it lacks a critical edition, there are no footnotes in the Quran to notify the reader about manuscript evidence or textual discrepancies or omissions, such that “(some verses eaten by a goat; Ibn Majah, Book of Nikah, p.39) or that (Umar records the missing verses; Bukhari 8.82.816 & 817).
Fourthly, Orientalists have often questioned the historical authenticity of the Quran by charging Uthman ibn Affan (the 3rd Caliph of Islam) of consigning variant copies of the Quran to the flames during his reign.
Fifthly, the controlled transmission of the Quran makes it impossible to know what was the original. Hence its textual integrity is seriously compromised. By contrast, in the case of the New Testament, for example, since no one person controlled all the manuscripts, it would be impossible to uniformly corrupt all the documents. In the case of the Quran, however, the text was in fact controlled by one person, the khalifa, as attested by Uthman's authority to recall and uniformly revise all the manuscripts. Therefore, it would have been extremely easy for the Quran to have been uniformly corrupted in a textually undetectable manner. For example, the “Sanaa manuscript,” which contains earlier developments of the Quran, demonstrates textual variances that diverge from the Uthman copy.
In conclusion, the Quran doesn’t allow us to come any closer to the original text than the Uthmanic Revised Standard Version 20 years removed from Muhammad. Any errors which found their way into the URSV would be permanent and uncorrectable. And, unfortunately, historical accounts from early Islam tell us that such errors existed!
——-
The Quran is Based on Dubious Sources
Besides the numerous and traceable Judeo-Christian apocryphal works that the author used within the Quran itself, he also got a lot of his ideas from a group that was an offshoot of the Ebionites called the “Sabians,” variously known as Mandaeans or Elcesaites. The Sabians followed Hermeticism and adored John the Baptizer:
Occasionally,
Mandaeans are called
‘Christians of Saint
John’ . . . the ‘Sabians’
are described several
times in the Quran as
People of the Book,
alongside Jews and
Christians (Wiki).
According to Origen and Eusebius, the Sabians used an extra-biblical book that they claimed was given by an Angel (maybe another idea adopted by Muhammad?) to deny portions of Scripture as well as the writings of Paul! So, this idea of challenging Christianity and claiming to have received a new revelation from an angel is quite common in ancient times. It is not unique to Islam. Others had made similar claims. Thus, without completely rejecting the possibility of *revelation* in at least some portions of the Quran, the majority of its theological narratives are largely based on dubious and questionable sources, derived from spurious texts that were under the radar of heresiologists across the ancient world!
——-
Two Apocryphal Works Employed by the Quran to Deny the Crucifixion of Jesus
//Second Treatise of the Great Seth is an apocryphal Gnostic writing discovered in the Codex VII of the Nag Hammadi codices and dates to around the third century. The author is unknown, and the Seth referenced in the title appears nowhere in the text. Instead Seth is thought to reference the third son of Adam and Eve to whom gnosis was first revealed, according to some gnostics. The author appears to belong to a group of gnostics who maintain that Jesus Christ was not crucified on the cross. Instead the text says that Simon of Cyrene was mistaken for Jesus and crucified in his place. Jesus is described as standing by and "laughing at their ignorance”// (Wiki).
//The Gnostic Apocalypse of Peter is a text found amongst the Nag Hammadi library, and part of the New Testament apocrypha. Like the vast majority of texts in the Nag Hammadi collection, it is heavily gnostic. It was probably written around 100-200 AD. Since the only known copy is written in Coptic, it is also known as the Coptic Apocalypse of Peter.
The text takes gnostic interpretations of the crucifixion to the extreme, picturing Jesus as laughing and warning against people who cleave to the name of a dead man, thinking they shall become pure. Like some of the rarer Gnostic writings, this one also doubts the established Crucifixion story which places Jesus on the cross. Instead, according to this text, there was a substitute:
He whom you saw on the
tree, glad and laughing,
this is the living Jesus.
But this one into whose
hands and feet they
drive the nails is his
fleshly part, which is the
substitute being put to
shame, the one who
came into being in his
likeness. But look at him
and me// (Wiki).
This is attested in the Quran:
That they said (in boast), ‘We killed Christ
Jesus the son of Mary, the Messenger of
Allah’—but they killed him not, nor crucified
him, but so it was made to appear to them,
and those who differ therein are full of
doubts, with no [certain] knowledge, but
only conjecture to follow, for of a surety they
killed him not—nay, Allah raised him up unto
Himself; and Allah is Exalted in Power,
Wise (Sura 4:157-158, Yusuf Ali).
——-
A Possible Forgery: Is Muhammad Copying Augustine?
Muhammad (570 – 632 CE) seems to have modelled his conversion on Augustine of Hippo (354 – 430 CE), who was without a doubt the greatest theologian and philosopher of his day! Case in point, in 386 CE, Augustine converted to Christianity from the pagan Machanean religion. Similarly, in 610 CE, Muhammad converted to Islam from the “Jahiliyya" religion, which worshipped Allah as the creator god as well as the Kaaba in Mecca. About 224 years earlier St. Augustine had heard a voice that told him to “take up and read,” a line which became very famous and reverberated through the centuries:
As Augustine later told it, his conversion
was prompted by hearing a child's voice
say ‘take up and read’ (Latin: tolle, lege).
Resorting to the Sortes Sanctorum, he
opened a book of St. Paul's writings (codex
apostoli, 8.12.29) at random and read
Romans 13: 13–14: Not in rioting and
drunkenness, not in chambering and
wantonness, not in strife and envying, but
put on the Lord Jesus Christ, and make no
provision for the flesh to fulfill the lusts
thereof (Wiki).
By comparison, Muhammad appears to have used a similar line to claim that he, too, heard an Angel’s voice repeatedly say to him: “Read.” Given that Muhammad was presumably familiar with Judaism and Christianity (and especially with the foremost leading authority of his day, the African Augustine of Hippo), it seems very likely that he modelled his conversion on the latter. And, if true, that would certainly constitute a forgery!
——-
Are Allah’s Oaths Self-contradictory in the Quran?
The aforementioned textual criticisms are further compounded when we realize that the Quran contains further theological discrepancies. For example, there are numerous verses in the Quran where Allah is swearing by created things that are less-than-God, thus committing “shirk” (i.e. the sin of ascribing divine status to any other beings beside Allah). Here’s a case in point. In sura 81:15, Allah says: “But nay! I swear by the stars.” Another example is sura 91 verse 1: “I swear by the sun and its brilliance.” When God supposedly swears by something which is less than himself the truth value of his assertion is obviously weakened. By definition, an oath is meant to buttress an argument, not to decrease the weight thereof. Therefore, the truth value of an oath is equivalent to, and connected with, the truth value of the one who declares it. As such, Allah’s oaths (swearing by created things) directly contradict his so-called divine status. By contrast, the God of the Bible swears by Himself, since there is nothing greater to swear under (cf. Gen. 22.16; Isa. 45.23; Heb. 6.13). By definition, an oath is a solemn attestation of the truth of one's words. In this case, how can Allah’s oaths be trustworthy if they appeal to something that is less than himself? Answer: they cannot! It appears, then, that the aforementioned oaths in the Quran are reflecting a human rather than a divine author.
——-
Is Muhammad the Prophesied False Prophet of Revelation?
During the Early Middle
Ages, Christendom
largely viewed Islam as a
Christological heresy
and Muhammad as a
false prophet (Wiki).
In short, following the Arab conquest of the Middle East and due to the *military expansion* of Islam into Europe and Central Asia since the 700’s (toppling one country after another), Muhammad was increasingly seen as a possible candidate for the office of the *false-prophet-of-Revelation* (cf. Rev. 16.13; 19.20; 20.10): https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Medieval_Christian_views_on_Muhammad

——-
Conclusion
Muslims claim that the Quran is neither corrupted nor influenced by Judeo-Christian sources, and yet upon further scrutiny the book clearly incorporates passages from both the Jewish Talmud and from various Christian apocryphal works. Plagiarism abounds, and so does forgery. Therefore, it is extremely difficult, if not impossible, to maintain that it’s a “revelation” when at least some of the sources of the Quran are highly dubious!
Moreover, Islam has nothing new to offer by way of revelation. Its doctrine could simply be classified as a modified theological redundancy of the Judeo-Christian tradition and the Biblical heritage that preceded it. The main difference between Islam and Christianity is this. Unlike the Quran’s singular witness and source——given that it was only revealed to *one* man (Muhammad)——the revelations of the New Testament were imparted to many different people, thereby authenticating its message by multiple attestations and witnesses!
——-

Is the Trinity a Biblical Teaching?
By Author Eli Kittim
“While the developed doctrine of the Trinity
is not explicit in the books that constitute
the New Testament, the New Testament
possesses a ‘triadic’ understanding of God
and contains a number of Trinitarian
formulas, including Matthew 28:19, 2
Corinthians 13:14, 1 Corinthians 12:4-5,
Ephesians 4:4-6, 1 Peter 1:2 and Revelation
1:4-5” (Trinity, Wiki).
The Deity of God the Father
To begin with, there are numerous New Testament verses which reveal God as “Father” (e.g., John 6:27, Titus 1:4). This fundamental concept of the Father as the creator and source of all living beings is of course famously attested in the Hebrew Scriptures with terms such as Yahweh and Elohim!
The Deity of Jesus Christ
We also have multiple texts which refer to the deity of Jesus Christ, depicting him as the so-called Son of God, such as in Jn 1:1 (“the word was God”), Col. 2:9 (“in him the whole fullness of deity dwells bodily”), Jn 8:58 (“before Abraham was, I am”), Heb. 1:3 (“The Son is the radiance of God’s glory and the exact imprint of his being”), Tit. 2:13 (“our great God and Savior Jesus Christ”), as well as the explicit worship Christ willingly received from his followers (Luke 24:52; John 20:28) and the accusations of blasphemy leveled against him for equating himself with God (Mark 2:7).
The Deity of the Holy Spirit
The personhood of the Holy Spirit is multiply-attested in the New Testament. There are many verses which hint at the deity of the Holy Spirit, calling Him, for example, a “person” (ἐκεῖνος, meaning “He” Jn. 16:13-14; ὁ Παράκλητος, which depicts “a person”; & ἐκεῖνος, meaning “he” Jn. 15:26). The Holy Spirit is also called the “eternal Spirit” (Heb. 9:14), a term that is often used interchangeably with the concept of God (1 Cor. 3:16; 6:19; Acts 5:3-4; Rom. 8:9; 2 Tim. 3:16; 2 Pet. 1:21). For example, the Holy Spirit is called “Lord” in 2 Corinthians 3:17:
“Now the Lord is the Spirit, and where the
Spirit of the Lord is, there is freedom.”
Moreover, the Holy Spirit is said to have insight into “the depths of God” (1 Corinthians 2:10-11). He also possesses knowledge (Romans 8:27). The Spirit is also said to have a personal will (1 Corinthians 12:11). He is capable of convicting the world of sin (John 16:8), and performs signs and miracles (Acts 8:39). He also guides (John 16:13) and intercedes between people (Romans 8:26). He utters commands and is also obeyed (Acts 10:19-20; 16:6). The Spirit talks (Revelation 2:7; 14:13; 22:17). He warns and prophesies of things to come (John 16:13; Acts 20:23). And the New Testament certainly depicts Him as a member of the Trinity (John 16:14; Matthew 28:19; 2 Corinthians 13:14).
The Plurality in the Godhead
What is more, the plurality in the Godhead is well attested not only in the New Testament but also in the Old Testament (Gen. 1:1-3, 26; Psalm 2:7; and Dan. 7:13-14)! Furthermore, there are many New Testament passages that either mention or allude to the Father, Son, and Holy Spirit as if they are distinct persons with different functions, yet equated in rank and status as a unit (Matt. 28:19; Gal. 4:6; 1 Cor.12:4-6; 1 Peter 1:1-2; 2 Cor. 13:14; Eph. 2:18; 3:14-17; 4:4-6; 5:18-20; 6:18). After all, Mt. 28:18-20 reads:
“And Jesus came and said to them, ‘All
authority in heaven and on earth has been
given to me. Go therefore and make
disciples of all nations, baptizing them in
the name of the Father and of the Son and
of the Holy Spirit, and teaching them to
obey everything that I have commanded
you. And remember, I am with you always,
to the end of the age.’ “
In Greek, 1 John 5:7 reads as follows:
ὅτι τρεῖς εἰσιν οἱ μαρτυροῦντες ἐν τῷ
οὐρανῷ ὁ πατὴρ ὁ λόγος καὶ τὸ ἅγιον
πνεῦμα καὶ οὗτοι οἱ τρεῖς ἕν εἰσιν.
(Stephens 1550 “Textus Receptus” aka
Received Text).
KJV Translation:
“For there are three that bear record in
heaven, the Father, the Word, and the Holy
Ghost: and these three are one.”
There has been much debate over 1 John 5:7 as to its authenticity (aka the “Johannine Comma”). Modern Bible versions that were formulated by mostly secular scholars in the 19th century, who largely denied the deity of Christ, used variant manuscripts (e.g., “Alexandrian texts”) to argue that 1 John 5:7 is an interpolation. However, scholars who have a high view of Scripture argue that the “Majority text” was more widely used by the early church and that this verse is in fact authentic and original.
The Trinity in the Hebrew Bible
A multiplicity of divine persons exists in the Hebrew Bible, as we find in Prov. 30:3-4, Gen. 35:1-7, as well as in Gen. 31:10-13 where the Angel of God is identified as God, no less!
Note the multi-personal God also in Eccles. 12:1 (YLT):
“Remember also thy Creators in days of thy
youth.”
While critics of the Triune God use Deut. 6:4 (The Shema) as a declaration of monotheism, this verse may also refer to a plurality of divine persons within the singular Godhead. The verse essentially reads:
Yahweh Elohenu Yahweh is one.
It Mentions God 3 times and then declares that he [is] one (echad). Besides mentioning God 3 times, the verse also uses the plural form ĕ·lō·hê·nū to suggest numerically more than one person. It’s tantamount to saying, Israel, pay attention to my declaration about God: one plus one plus one equals one (or 3 in 1)! Or, Yahweh, Elohenu, Yahweh = One (monotheism)! Elohenu is a noun, masculine plural construct, first person common plural. But what exactly does Deut. 6:4 mean when it says that God is one (echad)? Answer:
“Echad is the Hebrew word for one, but more
precisely it means a single entity but made
up of more than one part. There is another
Hebrew word from the same root – Yachid
which means single. The meaning of Echad
(more than one part) is a confirmation of
the Hebrew word Elohim which is translated
as God. Elohim is a plural word – more than
one . . .”
https://news.kehila.org/the-meaning-of-the-word-echad-one/

Moreover, Yahweh is not called qadosh (singular for ‘holy’) but qə·ḏō·šîm (plural) in Joshua 24:19 as well as in Prov. 9:10:
“The commencement of wisdom is the fear
of Jehovah, And a knowledge of the Holy
Ones is understanding.”
As for the distinction of the third person of the Trinity, namely, the Holy Spirit, besides 2 Sam. 23:2-3, read Isaiah 63:10-11:
“But they rebelled and grieved his holy spirit;
therefore he became their enemy; he
himself fought against them. Then they
remembered the days of old, of Moses his
servant. Where is the one who brought
them up out of the sea with the shepherds
of his flock? Where is the one who put
within them his Holy Spirit?”
Thus, the above-mentioned verses in the Hebrew Scriptures clearly support the theological concept of a plurality of persons within the singular Godhead, otherwise known as the Trinity.
The Plurality of Persons Within the Godhead Was Part of Judaism During the Time of Jesus
See my article: https://eli-kittim.tumblr.com/post/611381184411336704/the-two-powers-of-the-godhead-were-part-of-judaism


Preterism Debunked
By Eli Kittim
Was 70 CE the Worst Period Ever in the History of the Earth?
In talking about the great ordeal (aka “the great tribulation”), Mt. 24.21 says that there will be the greatest suffering ever in the history of the world before Jesus comes. 70 CE was not, by any stretch of the imagination, the worst period ever in the history of the earth. We have ample evidence of the Black Death (1346-1353), the Flu Pandemic (1918), and the two World Wars that killed over 100 million people, which were far worse than the destruction of Jerusalem in 70 CE. This fact alone severely weakens the Preterist argument of the imminent eschatology of Jesus and the apostles, which is characterised by the notion that the eschaton was supposed to take place in first century Palestine!
Similarly, Dan. 12.1, after discussing the worst period in the history of the earth, goes on to say that the resurrection of the dead will occur during the same time period (Dan. 12.2). Then, the Book of Daniel goes on to talk about “the time of the end” (12.4, 9), which obviously goes far beyond the first century. In point of fact, the Book of Daniel and the Gospel of Matthew offer two conspicuous examples which demonstrate that “the end of the days” (Dan. 12.13), or “the end” of human history (Mt. 24.14), is radically different than what the Preterist interpreters make it out to be, namely, a first century fulfillment. If anything, Scripture’s future end-time prophecies are meant to signal the ultimate dissolution of the universe (2 Pet. 3.10) and the creation of “a new heaven and a new earth” (Rev. 21.1). Events that obviously haven’t happened yet!
Could the Latter Years or The Day of the Lord Refer to the Time of Antiquity?
Biblically, the “eschaton” is set in the context of a future time-period that is intimately connected with “the day of the Lord” (ημέρα κυρίου)! And as regards the idiomatic expression, the Day of the Lord, almost all Bible scholars believe that it is an event that will take place at the end of the world (cf. Isa. 2.12; Ezek. 30.3; Joel 2.31-32; Amos 5.18-20; Zeph. 1.14-18; Acts 2.20). This, too, debunks the notion that the Day of the Lord was anticipated in the first century CE. Two Thessalonians 2.1-4 warns against such Preterist hypotheses by stating that the Day of Christ has not yet come, and that it won’t come until the arrival of the Antichrist at the end of days.
In fact, Preterism’s interpretative weakness can be exposed through many angles. For example, the end-times war known as the Gog-Magog war in Exekiel 38, which most prophecy experts ascribe to the future, is said to commence “in the latter years” (v. 8)! 70 CE certainly does not qualify as the latter years. It is untenable to suggest this hypothesis which does not fit with any of the end-time biblical prophecies and predictions.
Is the Terminal Generation the one that Will Not Pass Away Until All these Things Take Place?
Modern Greek linguistics demonstrate that “temporal values (past, present, future) are not established in Greek by use of the verbal aspects (or tense-forms) alone” (Stanley E. Porter, Idioms of the Greek New Testament [2nd edn; Sheffield: Sheffield Academic, 1999], p. 25). In other words, just because a verb is in the present tense doesn’t mean that the action is happening at present! So, this point demonstrates that the insistence on the present generation-interpretation does not necessarily square well with the authorial intent. For ex, the Johannine Jesus says figuratively that the hour “is now here, when the dead will hear the voice of the Son of God” (Jn. 5.25), and will come out of their graves. But we have no evidence that the resurrection of the dead happened in Antiquity. In fact, we have evidence that, according to Dan. 12.2, the resurrection of the dead is a future end-time event. Same with Mt. 24.34: “This generation will not pass away until all these things have taken place.” What things? Answer: all the future end-time events that are described in Mt. 24. Thus, Jesus is clearly describing the last generation on earth. For instance, the notion that some of Jesus’ followers would not die before they saw him coming in glory (16.27) or in his kingdom (Mt. 16.28) cannot be attributed to a supposed first-century CE context. Since Jesus has yet to come in his glory, it can only be ascribed to an eschatological spectrum of events. Since there is no historical record of these events ever taking place, the context of such passages is ultimately based not on preterism but futurism. In other words, the generation that is alive, at that future time, and sees these signs (as described in Mt. 24.33) is the same generation that will not die and witness the coming of the savior (cf. 1 Cor. 10.11)! In short, the timeline of “this generation” that “will not pass away” (Mt. 24.34) must be interpreted within the context of the prerequisite signs that will take place, not simply on linguistic grounds.
Translation and Exegesis of Biblical Greek Validates the Futurist Eschatology of the New Testament
If you add my particular contribution to the mix——where I discuss the explicit future eschatological verses in the Greek New Testament that refer to the end of the world——it turns out to be the final nail in the Preterist coffin! Phrases like τό πλήρωμα του χρόνου (Gal. 4.4; Eph. 1.10) refer to the final consummation when all things, both in the heavens and upon the earth, will conclude in Christ! Furthermore, the phrase επ´ εσχάτου των ημερων (Heb. 1.2) literally means “in the last days” and is an ipso facto reference to the end of the ages (cf. the alternative expression επ´ εσχάτου των χρόνων; 1 Pet. 1.20). These apocalyptic expressions are built on the term έσχατος (eschatos), which means “last in time.” In fact, the word eschatology is derived from the Greek term “eschaton.”
The Timeline of the Great Tribulation and the Resurrection of the Dead Does Not Square Well with the Apostolic Age
Many Biblical exegetes have traditionally misunderstood the inferred time-period associated with the phrase, “the time is near,” and have consequently assumed that both Jesus and the apostles expected the imminent end to happen in their lifetime. In fact, Bertrand Russell (the famous philosopher) wrote an essay indicating that he is not a Christian because, in his view, Jesus and the apostles were wrong about their imminent eschatology. These events never happened. Albert Schweitzer came to the same conclusion. Thereafter, many subsequent scholars followed suit.
(See the following article, which refutes this notion of imminent eschatology based on the koine Greek of the New Testament).

However, good exegesis requires that we evaluate the idiomatic expression “the time is near” (Rev. 1.3; 22.10) within its proper context, and therefore interpret it in light of the revelations that are associated with it. In other words, why is the warning in Rev. 22.10 not applicable to ancient times? Well, there are certain sign-posts that need to be deciphered first. And, in order to understand the particular timeline in question, we need a clear outline of the sequence of eschatological events. For example, the aforementioned apocalyptic locution “the time is near” is not mentioned in a vacuum as if it pertains to all generations, including that of the Apostolic Age, but rather in the context of the specific judgments of the tribulation period (see Rev. chs. 6–16). This specific tribulation period is inextricably connected to the “Beast” of Rev. 13, otherwise known as the “lawless one” (cf. 2 Thess. 2.3–4) or the Antichrist (1 Jn 2.18).
In order to ascertain the overall prophetic message of Revelation, the hermeneutical principle of the canonical context demands that we coalesce the different Biblical texts, as if we’re reading a single Book, rather than employing isolated, out-of-context passages to construct a subjective theology. For proper exegesis, we also need to use “the analogy of scripture,” rather than form opinions based on speculation and conjecture. In other words, we must allow scripture to interpret and define scripture. For instance, 2 Thess. 2.1–7 predicts a sequence of eschatological events in which the “Antichrist” will be revealed at roughly the same time as the “rapture,” the transporting of believers to heaven at the end of days. Incidentally, the rapture is said to occur contemporaneously with the general resurrection of the dead (cf. 1 Thess. 4.15–17). Since the general resurrection of the dead is an event that is associated with the apocalyptic time period known as the great tribulation——aka a period of “great suffering” (θλῖψις μεγάλη; Mt. 24.21; cf. Dan. 8.19; 12.1–2; Rev. 7.14)——2 Thess. 2.1-3 is teaching against the doctrine of imminence by stressing that the rapture and the resurrection cannot take place “unless the rebellion comes first and the lawless one is revealed.” Similarly, Daniel places the timeline of the resurrection in prophetic categories by stating that it will occur at the end of days (12.13)!
Let’s not forget that at the beginning of Matthew 24.3 a question is asked about the chronology of the signs of the times regarding these eschatological events:
“Tell us, when will this be, and what will be
the sign of your coming and of the end of
the age?”
It’s important to note, parenthetically, that the apocalyptic phrase “the end of the age” is actually a reference to the end of the world (see Mt. 13.39–40, 49; 24.3; 28.20). So, whatever eschatology one imposes on the New Testament, it must ultimately line up with the enumerated events discussed therein. By way of illustration, Mt. 24.21 says that the Great Tribulation (Gk. θλῖψις μεγάλη) will begin “when you see the desolating sacrilege standing in the holy place” (Mt. 24.15). This is further discussed in 2 Thess. 2.3–4 (cf. Dan. 9.27). Apparently, this is the same time period when the Great Tribulation will commence. Then, Mt. 24.29–31 goes on to discuss the “gathering” of the Son of Man’s elect (i.e. the rapture) within the time frame of the Great Tribulation (Gk. μετὰ τὴν θλῖψιν τῶν ἡμερῶν ἐκείνων). Therefore, the events of the rapture (1 Thess. 4.16–17) and the resurrection (Rev. 20.4–6) echo Daniel’s 12.1–2 reference regarding the general resurrection of the dead which must occur approximately in the same period of time as the phenomena of the Great Tribulation!
Further Evidence of Futurism from Revelation’s Global Wars & Geological Events
Further evidence that the eschatology of the New Testament is uniformly futurist, and not preterist, comes by way of the prophecy of the last empire on earth (Rev. 17.11), which has yet to come, that will play a major role during the time of the Great Tribulation (cf. Rev. 11.7; 12.3–6, 14; 17.9–13). Not to mention the prophetic references, in the Book of Revelation, to major geological events the scale of which has never before been seen in human history. For example, Rev. 6.14 alludes to how tectonic plates had been shifted to such an extent that “every mountain and island was removed from its place.” Revelation 16.20 adds that “every island fled away, and no mountains were to be found.” Such cataclysmic events have never been recorded before in human history! What is more, the descriptions in Luke 21 and the Book of Revelation pertain to global, not local, events. For example, Lk 21.10-11 talks about “Nation … against nation, and kingdom against kingdom,” and about earthquakes, plagues, and famines “in various places.” Revelation 6.8 tells us that “a fourth of the earth” will be wiped out “with sword, … famine, and plague.” Similarly, Rev. 6.15 mentions “the kings of the earth” and all of mankind seeking shelter “in the rocks of the mountains,” while Rev. 9.18 says that during this period “a third of mankind was killed by … three plagues.” Obviously, these are not local but global events. Incidentally, the phrase “was killed,” in Rev. 9.18, is a translation of the verb ἀπεκτάνθησαν, which is an aorist, indicative, passive, 3rd person plural form from ἀποκτείνω, meaning “to kill.” It is important to note that many verbs expressed in past tense, such as the aorist or the perfect-tense, do not actually tell us the timing of an event. There are, in fact, many perfect-tenses that are used for future prophecies. For example, Revelation 7.4 uses the perfect-tense τῶν ἐσφραγισμένων for those who “were sealed.” But this event obviously hasn’t happened yet. Similarly, Isaiah 53 is filled with past-tenses and yet it is a prophecy that Isaiah is writing about! Thus, a superficial reading of the text can often lead to erroneous interpretations.
Conclusion
Revelation 22.7, 9, 10, 18, and 19 repeats over and over again that this Book represents an exclusively prophetic Biblical text:
“Blessed is the one who keeps the words of
the prophecy of this book.”
This is also mentioned in the introduction (Rev. 1.3). Yet many Biblical expositors of a Preterist persuasion repeatedly violate Revelation’s reminder by interpreting certain events within a historical context, as if these events were expected to occur during the lifetime of the apostles. Not to mention that the Book of Revelation itself was written sometime around 96 CE and thus postdates the destruction of Jerusalem in 70 CE, which is often seen as the target date of the supposed eschaton.
As we have seen, good exegesis of “the time is near” phrase is only possible by way of the overall canonical context. Thus, Preterism involves a “proof-text fallacy” which comprises the idea of stringing together a number of out-of-context passages in order to validate the assumed imminent eschatology of the apostles. In other words, the Preterist conclusion is not compatible with the overall canonical context. This is equivalent to a coherence fallacy, that is to say, the illusion of Biblical coherence. Preterism also misinterprets the original Greek language of the New Testament, which is interested in the “aspect” rather than the “time” of an event.
I have outlined the overall canonical message of the Bible along with its specific prophetic content. So, when we look at all the prophetic predictions and combine them together to get a holistic understanding, we get a bigger picture of what will occur before the end. Therefore, how close we are to these events largely depends on how close we are to these prophetic signposts, temporally speaking. If you want to explore the prophetic markers of Mt. 24 from a historical perspective, see my article, Are We Living in the Last Days?

Therefore, Revelation’s caveat that “the time is near” is most certainly not a reference to first-century Christianity (cf. 1 Cor. 10.11; Mt. 24.3)! In light of this study, that interpretation would be completely false. Rather, it means that if the reader understands all the Biblical predictions and the specific end-time sequence of events as parts of an integrated whole, then he or she can properly infer if the time is near simply by discerning whether or not the major prophetic events of the New Testament have taken place on a global scale. A close reading of the apocalyptic genre of the New Testament reveals that it is not alluding to a first century fulfillment but to an end-time expectation!

How Old Was Abraham When He Left Haran?
By Bible Researcher Eli Kittim 🎓
The Apparent Contradiction
There’s a seeming contradiction in the Bible concerning Abraham’s age when he left Haran. The apparent contradiction is as follows. If Terah died when he was 205 years old, but fathered Abram when he was 70, then Abram must have been 135 years old when his father Terah died (as Gen. 11.26, 32 suggest), not 75, as Gen. 12.4 indicates. For the story to work without any discrepancies, Terah would literally have to be 130 years old when he fathered Abram. But it seemed as if he were only 70 years old. Hence the apparent contradiction. Below are the relevant citations that appear to contradict each other.
—-
Genesis 12.4 (ESV):
So Abram went, as the LORD had told him,
and Lot went with him. Abram was seventy-
five years old when he departed from
Haran.
Acts 7.2:
And Stephen said: ‘Brothers and fathers,
hear me. The God of glory appeared to our
father Abraham when he was in
Mesopotamia, before he lived in Haran.’
Acts 7.4:
Then he went out from the land of the
Chaldeans and lived in Haran. And after his
father died, God removed him from there
into this land in which you are now living.
Genesis 11.26:
When Terah had lived 70 years, he fathered
Abram, Nahor, and Haran.
Genesis 11.32:
The days of Terah were 205 years, and
Terah died in Haran.
—————
Apologetic Exegesis
The key passage is Gen. 11.26. The Hebrew text doesn’t explicitly say that *when* Terah was 70 years old he begat Abram. Rather, it puts it thusly (Gen. 11.26 KJV):
And Terah lived seventy years, and begat
Abram, Nahor, and Haran.
Nowhere is it explicitly mentioned that Terah had all 3 children when he was 70 years old. Nor is there any direct evidence that these children were triplets, or that they were born on the exact same date, month, or year. The verse in Gen. 11.26 merely indicates that after Terah reached a certain age——namely, 70 years old——he began to father children. But exactly when these children were actually born is unknown. The only thing that’s clear from Gen. 11.26 is that they were born after Terah had reached a certain age.
It’s quite possible, for example, that some of his children could have been born when Terah was 130 years old. Nothing in the text would contradict the timing of such a birth. As long as Terah fathered at least one child after he was 70, the rest could have been born anytime between Terah’s 70th and 205th birthday.
The order in which the names of Terah’s sons are listed may not reflect the precise chronological order in which the children were actually born. The text is simply indicating their order of importance. Given that Abram is a key figure in the Old Testament and the common patriarch of the Abrahamic religions, he’s obviously mentioned first:
there is yet a question whether Abram was
born first as listed, or perhaps he is listed
first because he was the wisest similar to
Shem, Ham, and Jafeth where Shem was
not the oldest, but was the wisest. … the
Talmud leaves the above question open.
(Wikipedia)
—————
Conclusion
Actually, Abram could have been 75 years old when he left Haran, as the text indicates (Gen. 12.4). And maybe he did leave Haran “after his father died” (Acts 7.4) at the age of 205 (Gen. 11.32). There is no contradiction with regard to the dates. The assumed contradiction is actually based on fallacious reasoning and speculation. It’s based on an eisegesis, that is, a misinterpretation of the text. Readers often assume that the text is telling us that Abram was born *when* Terah was 70 years old. But that’s a conjecture. The text doesn’t say that at all. All the text says is that once Terah reached a certain age, he began fathering sons. But exactly when each and every son was born is unknown.
—

How Should Christian Scholars Respond to Attacks and Insults?
By Bible Researcher and Author Eli Kittim 🎓
Now these people were more noble-minded
than those in Thessalonica, for they
received the word with great eagerness,
examining the Scriptures daily to see
whether these things were so.
——- Acts 17:11 NASB
Should We Believe What Others Say Or Should We Investigate the Scriptures for Ourselves?
People believe in historical Christianity. They believe that if Christianity is not historical then nothing else about the Bible is true. They cannot interpret it in any other way. They can only see it backwards; never forwards. But what ever happened to Bible prophecy? Take, for example, the idea of questioning the historicity of a Biblical event, wondering whether it happened in the past or if it will happen in the future. Isn’t that ultimately a question of faith?
People believe in a historical Jesus and in the so-called “historical” gospel narratives. Believers think that if Jesus didn’t exist——or if he didn’t die and wasn’t resurrected in the past——then everything else in the New Testament is complete and utter fiction, fabricated out of whole cloth, and therefore false. For them, it’s all about past history. But future history (aka Bible prophecy) is just as valid! The notion that Jesus came in the flesh *at some point in human history* somehow seems to escape their hermeneutical purview. It never really occurred to them that if these incidents in the life of Jesus are prophesied to take place in the future, then the Bible is just as valid and just as reliable as if these events had happened in the past. Why? Because the Bible is ultimately not a historical chronicle but a Book on Faith!
People believe what they hear. But sometimes that’s just fake news or long-held assumptions that are based on *wrong interpretations* of the facts. The story of Jesus’ past death and resurrection is a story that has been told millions of times at the dinner table, on television, during Christmas, Easter, in all churches and denominations, it’s heard from preachers in the pulpit, it’s repeated by missionaries, taught in seminaries, and has generally been reiterated by pastors and teachers throughout the culture for thousands of years. So, it’s as if it is written in stone. It’s a foregone conclusion. It’s considered to be an undeniable fact. But what if a thorough Biblical investigation challenged any of these points? What then? Mind you, this type of inquiry would only be challenging *the man-made interpretations,* not the actual words of the Bible per se!
——-
A Biblical Consensus Is Always Evolving
In science, the role of agreement is paramount in establishing empirical facts, and it’s only through verifiable evidence that an epistemic agreement can be reached. However, the body of empirical knowledge is constantly changing. New information is constantly assessed and prior conclusions are always re-examined. What appeared to be a fact yesterday may not be so today. And the methodology is constantly improving and evolving. Today, we have better criteria and more knowledge at our disposal to understand the Bible than ever before. Therefore, our biblical findings can certainly change our previous assumptions and presuppositions. The Biblical consensus has changed considerably over time. With new interdisciplinary evidence at our disposal, our conclusions about Biblical authorship and composition have gradually changed. New evidence in lower and high criticism has prompted new questions that require a new set of criteria and more advanced methodologies to address them. So, as a rule, new findings replace older “facts,” thereby changing the previous consensus!
For example, advances in textual criticism have shown that Moses was not the author of the Pentateuch. The date of the Pentateuch’s composition is also not as early as once believed. In fact, the scholarly consensus is that Moses probably never existed and that the Exodus never happened: it is a foundation myth. As it happens, no archaeological remains have ever been found in the Sinai Peninsula regarding the exodus or the Israelites.
But try telling that to Orthodox Jews who hold these “truths” to be self-evident, sacred, and non-negotiable. For them, history, archaeology, textual criticism, and Biblical studies are a “demonic” attempt to undermine their faith. But is that true? Of course not! On the contrary, many who are involved in these scientific and Biblical disciplines are themselves faithful Jews and Christians.
Then there was the emergence of other academic disciplines and methods that investigated the historical precursors of the biblical texts. Some of these were “source criticism” and “form criticism,” from which “redaction criticism” was derived. Finally, literary criticism added a new way of looking at the authorial intent via such methods as narrative criticism, rhetorical criticism, and canonical criticism. These emerging methods of biblical criticism, which did not previously exist, ultimately changed how we view and understand the Bible.
For example, the idea that the New Testament authors quoted predominantly from the Greek Old Testament rather than from the Jewish Bible must have certain important textual ramifications. Also, without the understanding of “intertextuality”——the literary dependence of the New Testament on the Old Testament——we would not know what literary material was borrowed from the Hebrew Bible. All you have to do is pick up a chain-reference Bible and you’ll see how much of the Old Testament is found in the New Testament, and how many words, speeches, and events that are attributed to Jesus are actually modelled on these earlier stories. These academic disciplines pave the way for a deeper understanding on various levels that heretofore were untraversed and unknown.
But how, then, can one explain to a believer that Jesus didn’t really say or do that? That it was just a literary narrative in which the evangelist put Jesus in a certain theological context in order to show that he is the prophesied Messiah of Hebrew Scripture. So, it seems that one must put away their emotional component when involved in this type of inquiry. One must leave their ego at the door. That is to say, one must temporarily suspend faith and atheism in dealing with Biblical studies. That’s because, just as in science, pure objectivity is strictly required. Once a person has gathered all the necessary evidence, they can then try to ascertain how it might fit with or be relevant to his/her faith, or how it may further inform it.
There are also many cross-reference and concordance studies that reveal Biblical *meanings* by focusing on certain repetitive linguistic idiomatic expressions, as they’re found throughout scripture. Parallel passages and verbal agreements help to further identify certain *meanings* that are consistently found across the text. Then there are the Biblical languages. Studying the original Biblical languages in Paleo-Hebrew and Koine Greek help us to create faithful and competent translations, which involve a more accurate knowledge and understanding of scripture’s details about timing, location, and authorial intention. Moreover, parsing (or syntax analysis) helps us to further understand the grammar and morphology of the Biblical languages! These methodologies are invaluable in providing a solid foundation that may not always be consistent with previous assumptions. Discoveries in these areas are obviously worthy of serious consideration.
But how do you explain these facts to a simple layperson who may think otherwise? In their eyes, you are seen either as a traitor to the faith, at best, or guided by the deceiver, at worst. To a believer——who is not engaged in these types of studies but reads the Bible literally and superficially——writing about these findings and complex issues may be interpreted as preaching godless heresies. In his/her mind you are simply a false teacher. . . And despite Jesus’ appeal for unity in the church (John 17:21), there have always been fights and quarrels among Christians (James 4:1). It has also become a fashion lately to slander Bible teachers. Many are quick to point fingers at each other and accuse other Christians of wrongdoing. This is antithetical to scripture!
In this case, the only thing a Bible scholar can do is to remind the reader that objectivity rather than fanaticism is more fruitful in biblical interpretation, and that name-calling is not biblical evidence. In fact, scholars welcome the opportunity for peer-review and academic criticism!

🔎 Bible Contradictions: In Using the Term “Arnion,” Does the Book of Revelation Contradict John’s Gospel Which Uses the Word “Amnos” Instead? 🔍
By Award-Winning Goodreads Author and Bible Researcher Eli Kittim 🎓
This short essay is a brief reply to a question that was posed by a member of my “Eli Kittim Theology” group on MeWe.
——-
The member’s name is Marlo Bliss. This was his Question:
The writer of the Book of Revelation used
the term "Lambkin" / ARNI'ON <G721> for
Jesus Christ instead of "lamb" / AMNO'S <>
(lambkins require feeding). He did so 26
times. Why this contradiction to John 1.29
and 1.36?
Thanks for any reply.
*I use the DLT (Dabhar Literal Translation)
software in hebrew, greek, english and
german.*
——-
He’s basically asking the following question: if John’s Gospel uses the Greek term Ἀμνὸς twice to refer to Jesus, then why does the Book of Revelation repeatedly use the word ἀρνίον instead? Isn’t that a deviation from the canonical context? Doesn’t that constitute a Biblical contradiction? The implication is that the Book of Revelation appears to be wrong and contradictory in its terminological usage.
First of all, it is important to establish at the outset that both ἀμνός (amnós) and ἀρνίον (arníon) mean the same thing. These terms are not self-contradictory, but rather interchangeable and complementary. Whereas **ἀμνός** (amnós) has the connotation of a consecrated or sacrificial lamb, especially a one-year old lamb, **ἀρνίον** refers to a “little lamb,” under a year old (Henry George Liddell. Robert Scott. A Greek-English Lexicon. Oxford. Clarendon Press. 1940). According to J. Thayer, the connotation of ἀρνίον (arníon) is that of pure innocence, with virgin-like (gentle) intentions.
Second, John’s Gospel uses both amnós and arníon. It’s true that John chapter 1 and verses 29 & 36 use the term Ἀμνὸς (lamb) to refer to Jesus Christ. But this term occurs only twice. And yet, the exact same gospel of John uses the alternative ἀρνία (lambs) in chapter 21 verse 15—-which is the plural form of the singular term ἀρνίον (lamb)——to refer to the *Christ-like* followers, namely, the saints of God who are becoming like Christ.
Third, the use of the word ἀρνίον (arníon) in a “messianic canonical context” is in fact scriptural, as can be seen, for example, in the Book of Jeremiah. In Jeremiah 11.19, the Septuagint (LXX) uses the Greek term ἀρνίον in an overtly messianic context:
ἐγὼ δὲ ὡς ἀρνίον ἄκακον ἀγόμενον τοῦ
θύεσθαι οὐκ ἔγνων ἐπ᾽ ἐμὲ ἐλογίσαντο
λογισμὸν πονηρὸν λέγοντες δεῦτε καὶ
ἐμβάλωμεν ξύλον εἰς τὸν ἄρτον αὐτοῦ καὶ
ἐκτρίψωμεν αὐτὸν ἀπὸ γῆς ζώντων καὶ τὸ
ὄνομα αὐτοῦ οὐ μὴ μνησθῇ ἔτι.
English translation by L.C.L. Brenton:
But I as an innocent lamb led to the
slaughter, knew not: against me they
devised an evil device, saying, Come and let
us put wood into his bread, and let us
utterly destroy him from off the land of the
living, and let his name not be remembered
any more.
This is reminiscent of Isaiah 53. In fact, Jeremiah’s aforementioned verse is a parallel to——and presents a near-verbal agreement with——Isaiah 53.7 (LXX):
καὶ αὐτὸς διὰ τὸ κεκακῶσθαι οὐκ ἀνοίγει
τὸ στόμα· ὡς πρόβατον ἐπὶ σφαγὴν ἤχθη
καὶ ὡς ἀμνὸς ἐναντίον τοῦ κείροντος αὐτὸν
ἄφωνος οὕτως οὐκ ἀνοίγει τὸ στόμα
αὐτοῦ.
Translation (NRSV):
He was oppressed, and he was afflicted,
yet he did not open his mouth; like a lamb
that is led to the slaughter, and like a sheep
that before its shearers is silent, so he did
not open his mouth.
In Jeremiah 11.19, the L.C.L. Brenton translates ἀρνίον “as an innocent lamb led to the slaughter,” while the NRSV similarly renders it as a “gentle lamb led to the slaughter.” The theological idea in Jeremiah 11.19 is consistent with that of Isaiah 53.7—-which says “like a lamb that is led to the slaughter”——even though Isaiah employs the terms πρόβατον (lamb) and ἀμνὸς (sheep) instead of Jeremiah’s use of the word ἀρνίον (lamb). These thematic parallels demonstrate that the above terms are interchangeable.
Thus, the Septuagint (LXX) uses 3 alternative terms to refer to this so-called messianic “lamb” of God who “was wounded for our transgressions, crushed for our iniquities; … and by his bruises we are healed” (Isaiah 53.5). Two of the three terms that the LXX uses for this *slaughtered messiah* are found in Isaiah 53.7, namely, πρόβατον and ἀμνὸς. Incidentally, πρόβατον (probaton) means ἀρνίον, which comes from ἀρήν (meaning “lamb”). Thus, ἀμνός (amnós), πρόβατον (próbaton), and ἀρνίον (arníon) are essentially interchangeable terms.
The word πρόβατον (probaton), which means ἀρνίον, is also used in Gen 22.8 by the LXX to refer to the sacrificial lamb of God:
Abraham said, ‘God himself will provide the
lamb for a burnt offering, my son.’ (NRSV)
The Septuagint also uses the Greek term πρόβατον (which means ἀρνίον) to refer to the sheep which is slaughtered as a “sin offering” in Lev 4.32.
Therefore, the Book of Revelation uses the exact same term that is found not only within the Biblical canonical-context itself (Jn 21.15), but also within the writings of the Septuagint as well. So how is it contradictory? It is not!
Conclusion
As you can see, the way in which the Koine Greek language has been used in both the Septuagint (LXX) and the New Testament clearly shows that the words ἀμνός (amnós), πρόβατον (próbaton), and ἀρνίον (arníon) are essentially interchangeable and complementary terms. These 3 words have all been used in terms of a “messianic sin offering,” that is, in reference to an innocent lamb that is led to the slaughter (cf. Rev. 5.6 ἀρνίον ἑστηκὸς ὡς ἐσφαγμένον/“a Lamb standing as if it had been slaughtered”). Although these terms have slightly different nuances, nevertheless they have been used consistently within a “messianic scriptural context” across the board. This is based on the principle of expositional constancy, the idea that similar terms and images are used consistently throughout scripture.
Since most scholars don’t think that John’s Gospel and the Book of Revelation were written by the same author, this would explain why they don't use the exact same terminology. Different biblical authors use different vocabularies. This fact alone doesn’t preclude their books from being seen as authoritative or inspired. On the contrary, if we look at the 27 New Testament books, this seems to be the rule rather than the exception!
Thus, Mr. Marlo Bliss’ accusation——that “the writer of the Book of Revelation [who] used the term "Lambkin" / ARNI'ON … for Jesus Christ instead of "lamb" / AMNO'S” was contradicting “John 1.29 and 1.36”——is unwarranted and without merit!
Incidentally, I looked at the so-called “DLT” (Dabhar Literal Translation) that Mr. Bliss uses, but unfortunately it is not faithful to the original Greek New Testament text. Besides, there is no disclosure or commentary about which text-types were used or if there even was a committee of scholars who edited it, which I seriously doubt, given the poor quality of the translation. I’ve also come across some YouTube videos, that are put out by the same sect, which endorse the Dabhar Literal Translation. Unfortunately, this English translation is of an inferior quality. Adherents of this cult further claim that the Book of Revelation is a “spurious” book. This sounds like a sect that has drifted away from sound Bible teaching!
——-

🚫 Millennialism Debunked
By Eli Kittim
The Contradictions of Millennialism
Millennialism is a belief that there will be a paradise here on earth before the final judgment. There are, of course, various scriptural discrepancies within this view, as I have often pointed out in my other papers. For example, how will people live here on earth if the earth itself will be destroyed in a great conflagration? 2 Pet. 3.10 reads:
“the heavens will pass away with a loud
noise, and the elements will be dissolved
with fire.”
Besides, there are other contradictions. For instance, how could the same people who would not be resurrected “until the thousand years were completed” (Rev. 20.5) simultaneously live and reign with Christ for a millennium? (Rev. 20.4). They cannot be both dead and alive at the same time! There are other contradictions as well. For example, Millennialism directly contradicts scripture by implying that there will be at least 2 additional comings of Christ, 2 appearances by Satan, 2 Great Wars, 2 Great tribulations, 2 resurrections, 2 apocalypses, 2 Armageddons, 2 judgments, 2 Great Ends, and so on. This is preposterous. In Scripture, there is only one of each. Scripture mentions only one resurrection (Dan. 12.2) and only one Armageddon (Rev. 16.16)! Where else does it mention a second resurrection or a second Armageddon? Besides, 1 Thess. 4.17 says that after the rapture “we will be with the Lord forever,” not just for 1,000 years. And the Book of Daniel is clear that both the Saved and the Damned will be resurrected simultaneously, not successively (12.2). Therefore, this DOUBLING of scriptural events is unwarranted and without merit! It is worth mentioning that the doctrine of millennialism was formally condemned at the Second Ecumenical Council in 381 AD.
Millennialism Repeats Events a Second Time; But Revelation is Recording Single Events
The same event that is mentioned in Ezekiel 38 is repeated in Revelation 20. The endtime Gog/Magog war that Satan is said to unleash at the end of the millennium (Rev. 20.8) is the exact same Gog/Magog war that is mentioned in Ezekiel 38, which is also alluded to in Luke 21.20! The Book of Revelation isn’t saying that the exact same Gog/Magog war of Ezekiel will repeat 1,000 years later. That’s ridiculous. It’s actually talking about one and the same Gog-Magog war; not 2. In fact, the phrase that is used to indicate that Satan will be released “for a little while” (Rev 20.3) is actually a reference to the Great Tribulation, which only lasts for “a little while,” namely, only 3 and a half years, or 42 months, or 1,260 days, or a time, and times, and half a time (cf. Rev. 11.2; 12.6, 14; 13.5)!
Moreover, the narrative in Rev 19 & 20 is basically telling the reader what will happen when God no longer restrains Satan (see 2 Thess 2.7)——that is, when the restrainer is removed——and the Antichrist is finally revealed at the end of a thousand years. That’s when Satan will be unleashed, once and for all, to wreak havoc “for a little while” (i.e. for 3 and a half years, during the Great Tribulation)!
Why would the Book of Revelation REPEAT the exact same story TWICE, like the film “Edge Of Tomorrow”? Why would Satan (Incarnated; Rev. 12.9) come out TWICE “to deceive the nations at the four corners of the earth [from the exact same location, Gog & Magog (Ezekiel 38)] in order to gather them for the [exact same] battle” (Rev. 20.7-9)? And why is it that “fire came down from heaven and consumed them” (Rev 20.9) exactly as it did in Ezekiel 38.22? And why is it that they “surrounded the camp of the saints and the beloved city” exactly as they did in Luke 21.20? Are you kidding me? What is this, a repeat of “Groundhog Day”?
There’s an Interpretive Mixup: Millennialists Conflate Scenes that Occur Before 1,000 Years with Scenes that Occur After 1,000 Years
If Jesus appears BEFORE the millennium on a white horse, and the beast and his armies are killed, and the beast is then captured and “thrown alive into the lake of fire” (Rev 19.19-21), then how does Satan manage to escape “the lake of fire” and mount a comeback? Notice that following Christ’s FIRST encounter with the Beast, BEFORE the millennium (Rev. ch. 20), the Beast was captured & immediately “thrown alive into the lake of fire” (Rev. ch. 19)! But the lake of fire is the second death! It’s game over! No one survives the lake of fire and comes back to to tell stories about it. That’s another red flag. It would be a scriptural contradiction to state that AFTER being “thrown into the lake of fire,” the Antichrist escaped and mounted a comeback. That would constitute a scriptural contradiction. Notice the description of the “lake of fire” in Rev. 20.14:
“Then Death and Hades were thrown into the
lake of fire. This is the second death, the
lake of fire.”
This event is final! It is the final separation of life and death. So, it’s completely bogus to say that Satan survived the lake of fire in chapter 19 & came back physically to fulfill chapter 20. It’s complete nonsense! Moreover, Satan’s activities in Rev. 20 suggest that he’s incarnate, otherwise how does a nonphysical being fight a war on earth? Besides, Rev. 12.9 tells us that Satan will be incarnated on earth! So, the Millennialists are mixing apples with oranges. They’re conflating scenes that happen BEFORE the 1,000 years (Rev. 19) with scenes that take place AFTER the 1,000 years (Rev. 20)! And if the description in Rev 20.10—-concerning what happens to Satan AFTER the supposed 1,000 years——turns out to be the exact same version of Rev 19.20—-about what happens to Satan BEFORE the 1,000 years——then we obviously have one story, not two!
Conclusion
The Bible never mentions the alleged “thousand-year reign of Christ on earth.” Only 2 verses mention those who “reigned with Christ a thousand years.” These are temporal signs that reveal the timing of Christ’s coming and of the apocalyptic events! In other words, when the thousand years are completed, Satan will be loosed for a little while (a reference to the 3 and a half year Great Tribulation). Then, the resurrection will occur, followed by the rapture, and the believers will henceforth reign with Christ forever!

The God-Messiah of the Old Testament
By Author Eli Kittim 🎓
In the original Hebrew text, Isaiah 9:6 paints a divine picture of the Messiah, unlike the one erroniously drawn by traditional Judaism of a mere human being. In particular, Isaiah 9:6 claims that the “son” (בֵּ֚ן ben) that is given to us is called “mighty” (גִּבּ֔וֹר gibbor) “God” (אֵ֣ל el). This is reminiscent of Leviticus 26:12 in which God **literally** promises to become **incarnated** as a human being:
I will also walk among you and be your
God.
What is more, in Isaiah 9:6 the Messiah is called “the Prince” (שַׂר־ sar), “the everlasting” (Hb. עַד “ad,” derived from “adah,” which means “perpetuity,” “continually,” or “eternally”). In other words, this “son” that “is given” to us is from everlasting. As a supplemental observation, compare the similarities of Micah 5:2 (NASB) regarding the Messiah:
His times of coming forth are from long ago,
From the days of eternity.
In other words, he is **uncreated**! The Septuagint (LXX), an early Greek translation of the Hebrew Bible, confirms this interpretation by also stating that this upcoming (messianic) ruler is from all **eternity.** In Micah 5:2 of the Septuagint (which is technically Micah 5:1 in the LXX), the prophecy is as follows:
ΚΑΙ σύ, Βηθλεέμ, οἶκος τοῦ ᾿Εφραθά,
ὀλιγοστὸς εἶ τοῦ εἶναι ἐν χιλιάσιν ᾿Ιούδα· ἐκ
σοῦ μοι ἐξελεύσεται τοῦ εἶναι εἰς ἄρχοντα
ἐν τῷ ᾿Ισραήλ, καὶ αἱ ἔξοδοι αὐτοῦ ἀπ᾿
ἀρχῆς ἐξ ἡμερῶν αἰῶνος.
English translation by L.C.L. Brenton:
And thou, Bethleem, house of Ephratha, art
few in number to be [reckoned] among the
thousands of Juda; [yet] out of thee shall
one come forth to me, to be a ruler of Israel;
and his goings forth were from the
beginning, [even] from eternity.
So we have compelling evidence from the very early Septuagint translation that the messiah to come is actually **uncreated,** and that he has existed from all **eternity.** This suggests that the “mighty God” of Isaiah 9:6, “the everlasting,” who is promised to become incarnated in Leviticus 26:12, is the same forthcoming messianic ruler that is mentioned in Micah 5:2 (Micah 5:1 LXX), whose “goings forth were from the beginning, [even] from eternity.”
Conclusion
Keep in mind that all this is coming from the Old Testament. We haven’t even touched the New Testament yet. Nevertheless, we find in the Old Testament numerous references to the messiah as an eternal, mighty, and incarnate God! And we haven’t even mentioned the deity of Jesus Christ in the New Testament:
In Jn 1:1 (‘the word was God’); Col. 2:9 (‘in
him the whole fullness of the godhead
[θεότητος] dwells bodily’); Heb. 1:3 (‘The
Son is the radiance of God’s glory and the
exact imprint of his being’); Tit. 2:13 (‘our
great God and Savior Jesus Christ’); ‘being
in very nature God’ (Phil. 2:6); ‘The Son is
the image of the invisible God’ (Col. 1:15);
‘our God and Savior Jesus Christ’ (2 Pet.
1:1); & in Jn 1:3 and Heb. 1:2 Jesus is the
creator and the ‘heir of all things, through
whom he [God] also created the worlds’; Jn
1:3: ‘All things came into being through him
[Jesus], and without him not one thing
came into being.’
Therefore, the eternal, timeless, uncreated, everlasting, almighty God (Rev. 1:8), who has always existed from all eternity, is the very same Creator-God who is promised to be born among us (Isa. 9:6; Mic. 5:2), and to “walk [וְהִתְהַלַּכְתִּי֙] among [בְּת֣וֹכְכֶ֔ם]” us (Lev. 26:12) “and be” our God!
The LXX was initially translated back in the 3rd century BC. This is clear evidence from the earliest sources that the messiah would be divine! The Micah 5:2 version of the LXX essentially confirms the DIVINE origin of the prophesied Messiah:
ἀπ᾽ ἀρχῆς ἐξ ἡμερῶν αἰῶνος.
It means that his origins are “from the beginning of days.” In other words, the messiah is the “Ancient of Days” (Aramaic: עַתִּיק יֹומִין, ʿatīq yōmīn; παλαιὸς ἡμερῶν, palaiòs hēmerôn), which is another name for God in Daniel 7:9!

“What is truth?” Pilate asked.
By Psychologist & Bible Researcher Eli Kittim 🎓
Feigned madness
Recently, I’ve had numerous Biblical debates with various people in many different groups. The topics were all different, but there was a common denominator: all my opponents refused to accept the indisputable and overwhelming evidence that I was presenting. This prompted me to seriously explore and investigate the cause of their reactions. In other words, when a scholar or a scientist provides irrefutable evidence that is not only obvious and clear but also demonstrably factual, then any refusal to accept it should be viewed as a form of mental illness or psychological neurosis. It can also be described as a *delusion*:
a persistent false … belief … that is
maintained despite indisputable evidence to
the contrary.
——- Merriam-Webster dictionary
It’s like giving someone all the facts that the earth is round, but they nevertheless still maintain that the earth is flat. Then there’s nothing further one can say. Anyone who pretends not to understand the evidence is therefore *feigning madness*:
‘Feigned madness’ is a phrase used in
popular culture to describe the assumption
of a mental disorder for the purposes of
evasion, deceit or the diversion of suspicion.
——- Wikipedia
It’s like a mathematician proving that 2+2 = 4. Only an insane person would disagree. Similarly, in one of my debates, I produced multiple lines of indisputable evidence to demonstrate that the pre-tribulational rapture is a false doctrine. Instead of accepting the evidence and thanking me for the proof-texts, my opponent got very irritable and hostile and started to insult me. He even called me a heretic. That’s when I knew I was dealing with a fanatic who probably had some form of mental illness. So, when a scholar or a scientist gathers the available body of facts about a particular topic and clearly demonstrates whether a belief or proposition is true or valid, then that should settle the matter, unless another scholar can disprove him. For example, when a belief or proposition is clearly proven to be false but certain people are unwilling to accept the evidence——to such an extent that they would even use insults to disrespect the researcher——then these people might be labeled fanatics. But what is actually happening psychologically is that these so-called “fanatics” who refuse to accept the overwhelming evidence are employing the defensive mechanism of *denial*:
Denial … is a psychological defense
mechanism postulated by psychoanalyst
Sigmund Freud, in which a person is faced
with a fact that is too uncomfortable to
accept and rejects it instead, insisting that
it is not true despite what may be
overwhelming evidence.
——- Wikipedia
It seems that a lot of people are deceived about a lot of things because they are essentially BIASED. That is to say, they’re not open to other views. The way this works is that they typically have an obstinate belief that they wish to maintain no-matter what, and so they are not interested in objective truth. They are only interested in maintaining their beliefs. So if people challenge their beliefs, they think that abandoning their beliefs would eventually lead to chaos. So they cling to their beliefs for dear life, even if these beliefs have been totally debunked. They’re not really interested in finding out whether their beliefs are true or false because that would entail a complete restructuring of their entire belief-system. So, instead of abandoning their current beliefs, which could lead to terrifying thoughts and emotions, they’d rather hold on to these false beliefs as a coping mechanism against a potentially hostile reality:
The theory of denial was first researched
seriously by Anna Freud. She classified
denial as a mechanism of the immature
mind because it conflicts with the ability to
learn from and cope with reality.
——- Wikipedia
Seeking Truth
But when something is proved to be false, shouldn’t we disregard it? If it doesn’t matter whether we prove it or not, then why bother debating at all? Why bother interpreting scripture or translating the Biblical languages? Why bother studying the Bible? If truth no longer matters, then why bother explaining scripture? Who cares? Many people typically say, “I don’t care what scholars say or what they can prove. I believe what I believe and that’s final.” Well, if truth no longer matters, then what’s the point of reading the Bible or following God? God might not exist & the Bible might be false. So why should we even bother reading about Christ if we’re no longer interested in truth?
What I am trying to get across is that “truth” must be the basis of everything we do! We must change our beliefs if they are found to be false. We shouldn’t entertain “beliefs” for their own sake but only because they can be demonstrated to be true! If our “beliefs” or “traditions” line up with truth, then we should accept them. But if they don’t, then we should reject them. You see, beliefs can be false, even deceptive and misleading. For example, many liberal pastors have crept into the church and are disseminating many FALSE BELIEFS as if they were true. That’s why so many people are deceived and confused. Many don’t even know what salvation is because of these false teachings. Bottom line, we should not be searching for “beliefs.” We should be searching for the “truth”! Paradoxically, when we find the truth, we will also find Jesus. And when we find Jesus, we will also find the truth. Why? Because the truth is not a principle; it’s a person:
Jesus said to him, ‘I am … the truth.’
——- John 14.6 (NASB)
So, “seeking” the truth is a noble path. In fact, we must be reborn into the truth. Rebirth is all about a new way of seeing (Jn 3.3), when we get rid of our false beliefs about God and meet him existentially. That’s when we come to realize that many of our beliefs about him are false. God then becomes a reality and teaches us new things about him that we never knew before (Jn 14.26).
What is Truth?
When we say that God’s word is “true,” we don’t mean that every story in the Bible is literally true. It could be a parable, a poem, or an allegory. Rather, we mean that the essence of God’s teachings (behind the narratives) is true. And when we do Biblical exegesis, we should always strive to see what we can prove; that is to say, what is true. Otherwise, there’s no point in trusting scripture or following God. We study scripture to prove it is true. And we follow God because we believe that he is truth itself. In other words, truth should be our guide and our teacher:
you will know the truth, and the truth will set
you free.
——- John 8.32
First kings 17.24 reminds us that “the word of the Lord … is truth.” In the same way, Psalm 25.5 prayerfully says, “Lead me in Your truth.” Psalm 45.4 similarly suggests that God himself fights “For the cause of truth” (cf. Rev. 19.11). Moreover, Psalm 119.160 says to God that “The sum of Your word is truth,” while Isaiah 65.16 calls him Elohim, “the God of truth.”
Interestingly enough, Jeremiah 9.3 compares good and evil to truth and falsehood (cf. Jer. 9.5). That’s why Dan 10.21 calls the Bible “the book of truth”! John 5.33 speaks of testifying to the truth. Notice that John 8.32 claims that the knowledge of the truth is what sets people free. By contrast, the devil “does not stand in the truth because there is no truth in him” (Jn 8.44). So the battle between good and evil turns out to be a battle between truth and falsehood. That’s precisely why the Holy Spirit is called “the Spirit of truth” (Jn 14.17). John 17.17 concludes that God’s “word is truth.” Thus, there is something special about truth that allows us to follow Christ. That’s why in his testimony before Pontius Pilate, Christ says:
Everyone who is of the truth listens to My
voice.
——- John 18.37
Therefore, we can rightly conclude that the difference between sinners and saints is the truth! How did people sin in the first place (according to Romans 1.25)? Answer: “they exchanged the truth of God for falsehood.” This means that the lies we believe are equivalent to sins. And if we are corrected but refuse to accept or even acknowledge the said edification, then we are deliberately sinning against God. Surprisingly, in Romans 2.8, truth is pitted against wickedness. That is to say, those who don’t obey the truth obey unrighteousness. In other words, being evil or morally wrong is directly related to a disobedience of the truth. That is why our defense against evil always involves criteria of truth (Eph. 6.14). As a matter of fact, 2 Thess. 2.10 attributes the state of damnation to a form of deception, in that those who are evil “did not accept the love of the truth so as to be saved.” So they will ultimately perish because they loved the lie more than the truth. Unlike Calvinism, which falsely preaches that God predestines people to hell, 1 Tim. 2.4 claims that God “wants all people to be saved and to come to the knowledge of the truth.” Therefore, *salvation* comprises a reception of “the knowledge of the truth.”
That’s why 2 Tim 1.14 is an exhortation to guard the truth that has been given to us by the Holy Spirit. Why should we guard the truth? Because if we believe a lie, it could be the difference between life and death; between salvation and damnation; between eternal life and eternal hell. Second Timothy 3.7 describes sinners as those who are “always learning and never able to come to the knowledge of the truth.” This means that one can have a vast amount of knowledge with regard to secular learning yet “never arrive at a knowledge of the truth.” First John 4.6 separates the open-minded from the close-minded people in terms of whether they possess “the spirit of truth” or “the spirit of error.” In other words, the ability to listen objectively with an open mind is somehow related to the Holy Spirit. That’s why holding on to deceptive doctrines and “paying attention to deceitful spirits and teachings of demons” (1 Tim. 4.1) is equivalent to the wide gate “that leads to destruction” (Mt. 7.13).
We know, for example, that we often deny the obvious truth because our defense mechanisms don’t allow us to hear it. That’s precisely why Jesus often says, “The one who has ears to hear, let him hear.” Only one question remains:
Are you willing to follow the *truth*
regardless of where it might lead?
——-

Who Wrote the Gospels? Are They Giving us History? Is Luke 1:1-4 a Case Study?
Eli Kittim
I think we need to seriously reevaluate our traditional view of the New Testament. Almost everything we believe about it is wrong. Christianity is not a historical religion, and it doesn’t need to be defended through archaeology or historical apologetics (e.g. listing eyewitnesses, or proving the resurrection), as is often done. Similarly, the gospels are not historical documents that correspond to real historical events. One would be hard put to reconstruct the so-called “historical Jesus” through fictional/theological stories that are largely based on the Old Testament.
For example, if Luke wrote his gospel based on other people’s opinions (Lk 1:1-4), we are in big trouble! Here’s what probably happened. There was no oral Aramaic tradition.
As scholars are now saying, the New Testament was probably written by the Greco-Roman literati (i.e. the educated upper class/intelligentsia). That’s precisely why the New Testament was composed, for the most part, in Greece and Rome. And that also explains why it was written in Greek by highly literate authors who didn’t understand the finer points of Jewish life in first century Palestine.
The New Testament authors must have been members of the Greco-Roman upper crust and very well-known, and that’s probably why they didn’t add their names to the texts. Some of the potential candidates who may have had a hand in writing the New Testament are Philo, Plutarch, and Josephus. And that’s probably why Luke seems to be familiar with Josephus’ works (Steve Mason). At any rate, it was obviously more than one writer, and all the authors, without exception, must have had transcendent experiences of God. There were no interviews and no “memories” involved, as Luke suggests. Every word they put on paper was coming directly from God. The New Testament is basically written in the form of prophetical writing (i.e. the genre called “apocalyptic literature”) because it’s based exclusively on visions and revelations (see Gal. 1:11-12; 1 Pet. 1:10-11)!
But we have completely misunderstood and misinterpreted these books. The problem is not with the New Testament; it’s with us. If you carefully analyze the New Testament, you’ll find that the epistles give us the “real” Jesus (meaning the actual *timing* of the parousia), whereas the gospels only give us a literary, fictional/theological rendering based on Old Testament material (intertextuality). That’s what’s going on!
Here’s the problem with our traditional interpretation of the preface to Luke’s Gospel. If Luke 1:1-4 is taken as prima facie evidence, then we’re no longer reading the word of God, but a case study. It’s as if Luke is saying: I interviewed someone, who knew someone, who knew someone, who knew one of the apostles. In other words, Luke is basing his gospel on the memories (or false memories) of some individuals. Is this the inspired word of God that we must now accept as eyewitness testimony? I think not!
There are many problems with that view.
First, if Luke is giving us reports from interviews, then his gospel would certainly not be considered as the inspired word of God, but rather a case study which contains the questionable memories of second generation Christians, who may or may not know much, or who may not remember things accurately.
Second, the composite work of Luke-Acts is a fictional composition. The Book of Acts, especially, creates a head-on collision with the authentic Pauline corpus, particularly with Galatians. Not to mention that many of the details in the story are seemingly fabricated (e.g. Pharisees working for Sadducees, the Sanhedrin had no jurisdiction in Syria, Paul’s journeys are contradicted, etc.), and even the term “Christian” was not used until the beginning of the 2nd century. That’s why scholars like EP Sanders and Paula Fredriksen view Acts as a work of historical fiction. In fact, Dr. Fredriksen seriously doubts whether the author of Luke-Acts was Paul's companion. According to her, Luke doesn’t seem to know Paul very well. Bottom line, if you want to understand the actual TIMING of the Birth, Death, and Resurrection of Jesus, read the epistles, not the gospels!
How Did God Inspire the Biblical Authors?


Is Mara bar Serapion’s Letter a Forgery?
Eli Kittim
The letter has been claimed to include no
Christian themes.
— Wiki
Mara bar Serapion was a stoic philosopher. He is noted for a lengthy letter that he wrote to his son. The letter was composed in Syriac, written sometime between 73 AD and the 3rd century. Many Christian apologists have suggested that Mara bar Serapion is alluding to Jesus Christ in this letter. But there are several problems with that theory.
First, a nonChristian like Mara bar Serapion would never have referred to Jesus as a “king.” Only dedicated and reborn Christians refer to Jesus as their Lord of lords and kings of Kings, not pagans.
Second, Jesus was not known as a “king.” In fact, according to Bruce Chilton and Craig A. Evans (“Studying the Historical Jesus,” pp. 455–457), “the term ‘king of the Jews’ has never been seen in the Christian literature of antiquity as a title for Jesus.”
Third, Jesus was not known as a “wise king.” The only Jew known to be a “wise king” was King Solomon, who was in fact a *king,* and whose *wisdom* was known throughout the ancient world. What is more, King Solomon is well known for being the author of many books of *wisdom* in the Bible.
Fourth, Mara bar Serapion does not even mention the terms “Jesus” or “Christ.” And when referring to famous heroic philosophers who died, and what happened after their death, he never mentions Jesus’ resurrection. Even if he didn’t believe it, he would have, at least, mentioned the *rumor* of Jesus being raised from the dead. The fact that he doesn’t mention it at all means that he’s not talking about Jesus:
[Robert E.] Van Voorst adds two factors
that indicate Mara was not a Christian, the
first being his failure to mention the terms
Jesus or Christ. The second factor (also
supported by Chilton and Evans) is that
Mara's statement that Jesus lives on based
on the wisdom of his teachings, in contrast
to the Christian concept that Jesus
continues to live through his resurrection,
indicates that he was not a Christian.
— Wiki
Fifth, the language of the document suggests that Mara bar Serapion is referring to an actual king who enacted new laws and established new practices. For example, Jewish tradition ascribes ritual hand washing and eruvin to King Solomon, who also served as a Judge (e.g. the “Judgment of Solomon”). He was also responsible for building the first temple, and for instituting new laws of how the temple services would run:
Nay, Socrates did ‘not’ die, because of
Plato; nor yet Pythagoras, because of the
statue of Hera; nor yet the Wise King,
because of the new laws which he enacted.
— Wiki
Sixth, there’s something very odd about the reference to the Jews in this letter. This is quite a long letter, which is based entirely on Greek philosophy. Scholars are in agreement that Mara bar Serapion was a Stoic philosopher and a pagan. As a rule, Stoic philosophers held Jewish teachings in contempt, and so they would never have placed them on a par with the teachings of Socrates, Plato, and Pythagoras. We know this from the apostle Paul who was scoffed at when preaching to stoic philosophers in Athens (Acts 17:15-34). The addition of the “Jewish” element, therefore, reads like a non sequitur, like a strange interpolation that doesn’t belong there… It sounds as if someone added it at a later time. And it seems as if the author (or editor?) got things wrong. Pythagoras was not burned, and King Solomon was not killed. And the expulsion of the Jews might be a reference to the deportation of the Northern Kingdom in 722 BC, or to that of Judah in 586 BC:
The letter refers to the unjust treatment of
‘three wise men’: the murder of Socrates,
the burning of Pythagoras, and the
execution of ‘the wise king’ of the Jews.
— Wiki
Now that I have offered my critique, let’s actually read that portion of the letter that apologists have employed time after time as evidence for the historicity of Jesus. Do you think that this pericope constitutes strong evidence for the existence of Jesus? Hardly! Not by a long shot:
For what benefit did the Athenians obtain
by putting Socrates to death, seeing that
they received as retribution for it famine and
pestilence? Or the people of Samos by the
burning of Pythagoras, seeing that in one
hour the whole of their country was covered
with sand? Or the Jews by the murder of
their Wise King, seeing that from that very
time their kingdom was driven away from
them? For with justice did God grant a
recompense to the wisdom of all three of
them. For the Athenians died by famine;
and the people of Samos were covered by
the sea without remedy; and the Jews,
brought to desolation and expelled from
their kingdom, are driven away into every
land. Nay, Socrates did “not” die, because
of Plato; nor yet Pythagoras, because of the
statue of Hera; nor yet the Wise King,
because of the new laws which he enacted.
— Wiki
Eli Kittim Reddit
