If We Get Some Kind Of Reunion Between These Two In Btsv Ill Bawl My Eyes Out
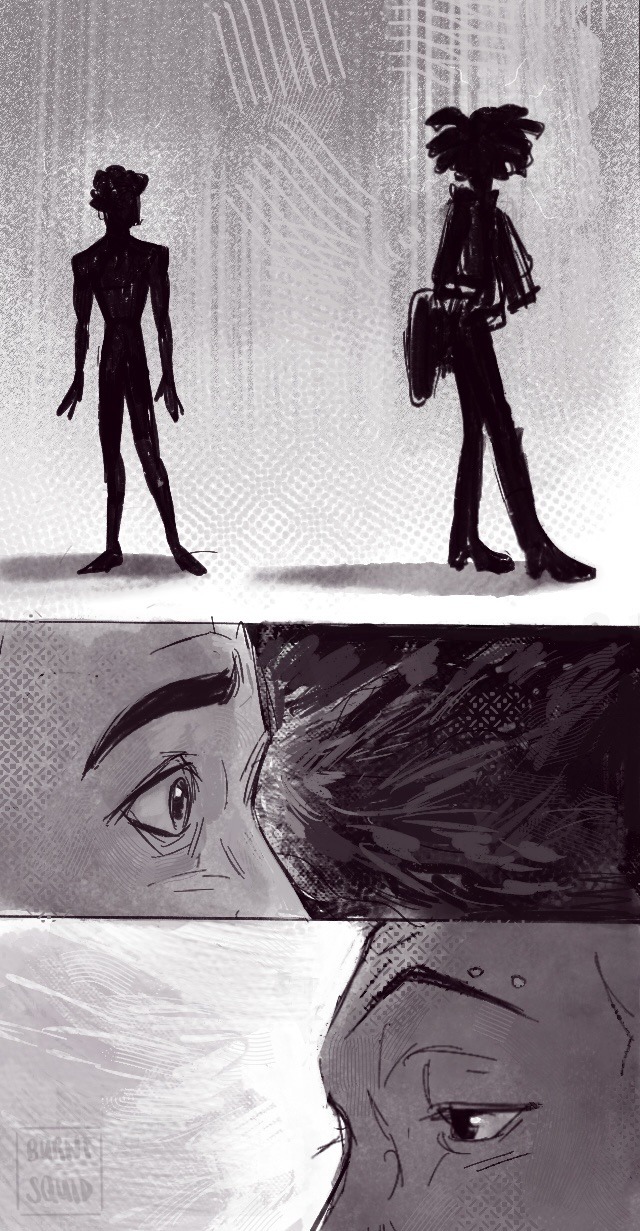


if we get some kind of reunion between these two in btsv i’ll bawl my eyes out
-
 stuntingonthelow reblogged this · 1 year ago
stuntingonthelow reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 audhdcouchpotato liked this · 1 year ago
audhdcouchpotato liked this · 1 year ago -
 pasteldaifuku liked this · 1 year ago
pasteldaifuku liked this · 1 year ago -
 benclassy-blog1 liked this · 1 year ago
benclassy-blog1 liked this · 1 year ago -
 katedeville liked this · 1 year ago
katedeville liked this · 1 year ago -
 collectivelycornflakes reblogged this · 1 year ago
collectivelycornflakes reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 mossysoupfrog liked this · 1 year ago
mossysoupfrog liked this · 1 year ago -
 luvpunkflower reblogged this · 1 year ago
luvpunkflower reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 luvpunkflower liked this · 1 year ago
luvpunkflower liked this · 1 year ago -
 hotgaybitch liked this · 1 year ago
hotgaybitch liked this · 1 year ago -
 coldhe3rt14 reblogged this · 1 year ago
coldhe3rt14 reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 coldhe3rt14 liked this · 1 year ago
coldhe3rt14 liked this · 1 year ago -
 visions--of--collisions reblogged this · 1 year ago
visions--of--collisions reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 shaun-lara liked this · 1 year ago
shaun-lara liked this · 1 year ago -
 aliaa-j liked this · 1 year ago
aliaa-j liked this · 1 year ago -
 murconstellation reblogged this · 1 year ago
murconstellation reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 lemontea2 liked this · 1 year ago
lemontea2 liked this · 1 year ago -
 xxhot-mindsxx85 reblogged this · 1 year ago
xxhot-mindsxx85 reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 killer-blubber34 liked this · 1 year ago
killer-blubber34 liked this · 1 year ago -
 ejamo reblogged this · 1 year ago
ejamo reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 ejamo liked this · 1 year ago
ejamo liked this · 1 year ago -
 davidbowiestuff liked this · 1 year ago
davidbowiestuff liked this · 1 year ago -
 blessed-rose liked this · 1 year ago
blessed-rose liked this · 1 year ago -
 inkyd00dle liked this · 1 year ago
inkyd00dle liked this · 1 year ago -
 pastelia-sprinkles liked this · 1 year ago
pastelia-sprinkles liked this · 1 year ago -
 blackbirdloki liked this · 1 year ago
blackbirdloki liked this · 1 year ago -
 meomwem liked this · 1 year ago
meomwem liked this · 1 year ago -
 peniwinklethebaddog liked this · 1 year ago
peniwinklethebaddog liked this · 1 year ago -
 etheralunaiza liked this · 1 year ago
etheralunaiza liked this · 1 year ago -
 moldymotherfucker liked this · 1 year ago
moldymotherfucker liked this · 1 year ago -
 tinytimetravelcandy liked this · 1 year ago
tinytimetravelcandy liked this · 1 year ago -
 thestarsspeaktome liked this · 1 year ago
thestarsspeaktome liked this · 1 year ago -
 join-my-marvel-cult liked this · 1 year ago
join-my-marvel-cult liked this · 1 year ago -
 emmabrooke03 liked this · 1 year ago
emmabrooke03 liked this · 1 year ago -
 loki-wants-an-army liked this · 1 year ago
loki-wants-an-army liked this · 1 year ago -
 sweetconnoisseurgiver liked this · 1 year ago
sweetconnoisseurgiver liked this · 1 year ago -
 spirited-splashes liked this · 1 year ago
spirited-splashes liked this · 1 year ago -
 cricketblabbers liked this · 1 year ago
cricketblabbers liked this · 1 year ago -
 monkey-zone liked this · 1 year ago
monkey-zone liked this · 1 year ago -
 fandom-nerd5225 liked this · 1 year ago
fandom-nerd5225 liked this · 1 year ago -
 bunnyboo132 liked this · 1 year ago
bunnyboo132 liked this · 1 year ago -
 amc-namt liked this · 1 year ago
amc-namt liked this · 1 year ago -
 sunsets-on-water reblogged this · 1 year ago
sunsets-on-water reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 genderblentbeeper liked this · 1 year ago
genderblentbeeper liked this · 1 year ago -
 blahwithasideofblah reblogged this · 1 year ago
blahwithasideofblah reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 illeii liked this · 1 year ago
illeii liked this · 1 year ago -
 slaughterfreak liked this · 1 year ago
slaughterfreak liked this · 1 year ago -
 moonlightalan07 reblogged this · 1 year ago
moonlightalan07 reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 pinkiepuunk liked this · 1 year ago
pinkiepuunk liked this · 1 year ago -
 appleyescream liked this · 1 year ago
appleyescream liked this · 1 year ago
More Posts from Transgirl-from196

Title: Neptune Basin, Versailles
Artist: James Carroll Beckwith
Date: 1913
Genre: Landscape

Silhouette Tree

Angus McKie's cover art for The High Frontier: Human Colonies in Space by Gerard K. O'Neill, 1978.

Navigating Deep Space by Starlight
On August 6, 1967, astrophysicist Jocelyn Bell Burnell noticed a blip in her radio telescope data. And then another. Eventually, Bell Burnell figured out that these blips, or pulses, were not from people or machines.

The blips were constant. There was something in space that was pulsing in a regular pattern, and Bell Burnell figured out that it was a pulsar: a rapidly spinning neutron star emitting beams of light. Neutron stars are superdense objects created when a massive star dies. Not only are they dense, but neutron stars can also spin really fast! Every star we observe spins, and due to a property called angular momentum, as a collapsing star gets smaller and denser, it spins faster. It’s like how ice skaters spin faster as they bring their arms closer to their bodies and make the space that they take up smaller.

The pulses of light coming from these whirling stars are like the beacons spinning at the tops of lighthouses that help sailors safely approach the shore. As the pulsar spins, beams of radio waves (and other types of light) are swept out into the universe with each turn. The light appears and disappears from our view each time the star rotates.

After decades of studying pulsars, astronomers wondered—could they serve as cosmic beacons to help future space explorers navigate the universe? To see if it could work, scientists needed to do some testing!
First, it was important to gather more data. NASA’s NICER, or Neutron star Interior Composition Explorer, is a telescope that was installed aboard the International Space Station in 2017. Its goal is to find out things about neutron stars like their sizes and densities, using an array of 56 special X-ray concentrators and sensitive detectors to capture and measure pulsars’ light.

But how can we use these X-ray pulses as navigational tools? Enter SEXTANT, or Station Explorer for X-ray Timing and Navigation Technology. If NICER was your phone, SEXTANT would be like an app on it.
During the first few years of NICER’s observations, SEXTANT created an on-board navigation system using NICER’s pulsar data. It worked by measuring the consistent timing between each pulsar’s pulses to map a set of cosmic beacons.

When calculating position or location, extremely accurate timekeeping is essential. We usually rely on atomic clocks, which use the predictable fluctuations of atoms to tick away the seconds. These atomic clocks can be located on the ground or in space, like the ones on GPS satellites. However, our GPS system only works on or close to Earth, and onboard atomic clocks can be expensive and heavy. Using pulsar observations instead could give us free and reliable “clocks” for navigation. During its experiment, SEXTANT was able to successfully determine the space station’s orbital position!

We can calculate distances using the time taken for a signal to travel between two objects to determine a spacecraft’s approximate location relative to those objects. However, we would need to observe more pulsars to pinpoint a more exact location of a spacecraft. As SEXTANT gathered signals from multiple pulsars, it could more accurately derive its position in space.

So, imagine you are an astronaut on a lengthy journey to the outer solar system. You could use the technology developed by SEXTANT to help plot your course. Since pulsars are reliable and consistent in their spins, you wouldn’t need Wi-Fi or cell service to figure out where you were in relation to your destination. The pulsar-based navigation data could even help you figure out your ETA!

None of these missions or experiments would be possible without Jocelyn Bell Burnell’s keen eye for an odd spot in her radio data decades ago, which set the stage for the idea to use spinning neutron stars as a celestial GPS. Her contribution to the field of astrophysics laid the groundwork for research benefitting the people of the future, who yearn to sail amongst the stars.
Keep up with the latest NICER news by following NASA Universe on X and Facebook and check out the mission’s website. For more on space navigation, follow @NASASCaN on X or visit NASA’s Space Communications and Navigation website.
Make sure to follow us on Tumblr for your regular dose of space!

