
216 posts
Sean Bienvenidos, Japonistasarqueologicos A Una Nueva Entrega De Historia Nipona En La Que Os Pongo Imgenes







Sean bienvenidos, japonistasarqueologicos a una nueva entrega de historia nipona en la que os pongo imágenes de los epicentros tras los bombardeos del 6 y 9 de agosto, una vez dicho esto pónganse cómodos que empezamos. - Antes que nada me gustaría poner un poco de contexto histórico para poder entender la situación, Japón estaba perdiendo la guerra y estaban buscando formas desesperadas para frenar el avance norteamericano que se cernía sobre el país del sol naciente. Recurrirán a los kamikazes vía aérea y terrestre de hecho se estaba preparando en Japón unas fuerzas de defensa con mujeres, tras la batalla de Okinawa en los 82 días de combate murieron cerca de 100.000 soldados japoneses, más de 12.000 estadounidenses y al menos 100.000 civiles locales, incluidos cientos que fueron obligados a matarse a sí mismo, también se perdería el Yamato en el último kamikaze. - Ciudad de Hiroshima:6 de agosto 1945, Little Boy fue arrojado desde el Enola Gay, matando a más de 70.000 personas al instante y muchas más morirían consecuencia de la radiación. Ciudad de Nagasaki: 9 de agosto 1945, Fat Man, fue la otra bomba atómica lanzada por el mismo avión, causando la muerte de 49.000 personas el día de la explosión. - Conclusión: Los costos fueron terribles, ya que las propias consecuencias lo fueron aún más, espero que no se tengan más bombas atómicas, ni de cualquier otro tipo, el ser humano debería aprender de los errores de la historia para que se acabaran las guerras. Publicación en memoria de todos los que murieron por las bombas atómicas. - Esperó que os haya gustado y nos vemos en próximas publicaciones que pasen una buena semana. - 日本の考古学者の皆さん、ようこそ日本史の新連載へ。8月6日と9日の原爆投下後の爆心地の画像をお届けします。 - まず最初に、この状況を理解するために歴史的背景を説明したいと思う。日本は戦争に負け、日出ずる国に迫りつつあったアメリカの進撃を食い止めるための絶望的な方法を模索していた。沖縄戦の後、82日間の戦闘で10万人近くの日本兵が死に、1万2000人以上のアメリカ兵と、自殺を余儀なくされた数百人を含む少なくとも10万人の民間人が亡くなった。 - 広島市:1945年8月6日、エノラ・ゲイからリトルボーイが投下され、7万人以上が即死。長崎市:1945年8月9日、ファットマンが同じ飛行機から投下され、爆発当日に49,000人が死亡した。 - 結論:原爆投下は、その結果そのものもさることながら、その代償もまた恐ろしいものであった。 私は、原爆や他のいかなる種類の爆弾もこれ以上投下されないことを願うとともに、人類が歴史の過ちから学び、戦争がなくなることを願っている。原爆で亡くなられたすべての方々を悼んで。 - お気に召していただけたなら幸いである。 良い一週間を. - Welcome, Japanese archaeologists, to a new instalment of Japanese history in which I bring you images of the epicentres after the bombings of 6 and 9 August, so make yourselves comfortable and let's get started. - First of all I would like to give some historical context to understand the situation, Japan was losing the war and they were looking for desperate ways to stop the American advance that was looming over the land of the rising sun. They resorted to kamikazes by air and land in fact they were preparing in Japan a defence force with women, after the battle of Okinawa in the 82 days of combat nearly 100,000 Japanese soldiers died, more than 12,000 Americans and at least 100,000 local civilians, including hundreds who were forced to kill themselves, they would also lose the Yamato in the last kamikaze. - Hiroshima City: 6 August 1945, Little Boy was dropped from the Enola Gay, killing over 70,000 people instantly and many more would die from radiation. Nagasaki City: 9 August 1945, Fat Man, was the other atomic bomb dropped from the same plane, killing 49,000 people on the day of the explosion. - Conclusion: The costs were terrible, as the consequences themselves were even more so. I hope that there will be no more atomic bombs, or any other type of bomb, and that mankind should learn from the mistakes of history so that wars will end. Publication in memory of all those who were killed by atomic bombs. - I hope you liked it and see you in future publications. Have a good week.
-
 kerovousphoto liked this · 1 year ago
kerovousphoto liked this · 1 year ago -
 buffetlicious liked this · 1 year ago
buffetlicious liked this · 1 year ago -
 rfpreiwaphase reblogged this · 1 year ago
rfpreiwaphase reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 repera23 liked this · 1 year ago
repera23 liked this · 1 year ago -
 ihsanperfectlysparklywolf liked this · 1 year ago
ihsanperfectlysparklywolf liked this · 1 year ago -
 vestaignis liked this · 1 year ago
vestaignis liked this · 1 year ago -
 divorce liked this · 1 year ago
divorce liked this · 1 year ago -
 danielrexi liked this · 1 year ago
danielrexi liked this · 1 year ago -
 vivencias-del-alma liked this · 1 year ago
vivencias-del-alma liked this · 1 year ago -
 takanaminato liked this · 1 year ago
takanaminato liked this · 1 year ago -
 bear-pattern-hamster liked this · 1 year ago
bear-pattern-hamster liked this · 1 year ago -
 noticiasarquelogicasjaponesas reblogged this · 1 year ago
noticiasarquelogicasjaponesas reblogged this · 1 year ago -
 famousinuniverse liked this · 1 year ago
famousinuniverse liked this · 1 year ago -
 naser1963 liked this · 1 year ago
naser1963 liked this · 1 year ago -
 rodolfo9999 liked this · 1 year ago
rodolfo9999 liked this · 1 year ago -
 asongpanda1 liked this · 1 year ago
asongpanda1 liked this · 1 year ago -
 narihira8 liked this · 1 year ago
narihira8 liked this · 1 year ago -
 nostalblue liked this · 1 year ago
nostalblue liked this · 1 year ago -
 u-nobu liked this · 1 year ago
u-nobu liked this · 1 year ago -
 hiromusicarts-blog liked this · 1 year ago
hiromusicarts-blog liked this · 1 year ago
More Posts from Noticiasarquelogicasjaponesas



Sean bienvenidos a un nueva entrega un tanto especial, ya que tengo el gusto de presentaros Ishibutai, localizado en la prefectura de Nara data del periodo Asuka(592-710). - En un principio se barajaron hipótesis de que podría haber sido utilizado para espectáculos, en la década de los 30, Ishibutai es un kofun y os estaréis preguntando ¿no se supone que tenían ojo de cerradura? - Los podian a ver de muchos tipos se empiezan a construir en el año 300 al 592 d.c pero eso será otro capítulo de la arqueología y prehistoria japonesa. La tumba pudo pertenecer a Soga no Umako un político y ocupa una extensión de 54 m es la mayor estructura megalítica conocida en Japón. - ¿Hasta cuando estuvo utilizada? la edad de uso os dejará helados se construyó en el siglo VI y estuvo hasta el siglo VII para ser más exactos en este segundo dato en el 626 d.c. - En 1957 fue nombrado patrimonio nacional por la Unesco, ¿Cuánto pesa esta mole? un total de 30 rocas que le suman un peso aproximadamente de 2300 toneladas y las piedras del techo suman una friolera de 77 toneladas aproximadamente. - Espero que os haya gustado y nos vemos en una nueva publicación de arqueología y prehistoria arqueología japonesa. - Welcome to a new, somewhat special installment, as I have the pleasure of introducing you to Ishibutai, located in the Nara prefecture, dating from the Asuka period (592-710). - At first, hypotheses were considered that it could have been used for shows, in the 1930s, Ishibutai is a kofun and you may be wondering, aren't they supposed to have a keyhole? - You could see them of many types, they began to be built in the year 300 to 592 AD but that will be another chapter of Japanese archeology and prehistory. The tomb could have belonged to Soga no Umako, a politician, and occupies an area of 54 m, it is the largest megalithic structure known in Japan. - Until when was it used? The age of use will leave you frozen. It was built in the 6th century and was there until the 7th century to be more exact in this second data in 626 AD. - In 1957 it was named a national heritage site by UNESCO. How much does this mass weigh? a total of 30 rocks that add up to a weight of approximately 2,300 tons and the stones of the roof add up to a whopping 77 tons approximately. - I hope you liked it and see you in a new publication of archeology and prehistory Japanese archaeology. - 新しい、ちょっと特別な回へようこそ。今回は、飛鳥時代 (592 ~ 710 年) に遡る、奈良県にある石舞台についてご紹介したいと思います。 - 当初は、1930 年代にショーに使用されたのではないかという仮説が考えられていました。 石舞台は古墳ですが、鍵穴があるはずではないかと疑問に思うかもしれません。 - さまざまなタイプのそれらを見ることができ、それらは西暦 300 年から 592 年に建てられ始めましたが、それは日本の考古学と先史学の別の章となるでしょう。 この墓は政治家蘇我馬子の墓と考えられ、面積は54メートルあり、知られている巨石建造物としては日本最大である。 - いつ頃まで使われていましたか? この 2 番目のデータは西暦 626 年で、6 世紀に建てられ、より正確には 7 世紀まで存在していました。 - 1957 年にユネスコによって国家遺産に指定されましたが、この塊の重さはどれくらいでしょうか? 30 個の石を合計すると約 2,300 トン、屋根の石を合計すると約 77 トンにもなります。 - 気に入っていただければ幸いです。考古学と先史時代の日本の考古学の新しい出版物でお会いしましょう。






Sean bienvenidos japonistasarqueologicos, a una nueva entrega de arqueología nipona, en esta ocasión os enseñaré algunos objetos recuperados del yacimiento del toro, entre otros — Los bienes muebles: son todos aquellos materiales que están hechos de madera y hueso que rara vez se conservan, a no ser que se den las condiciones óptimas como es en este caso. Pondré en un orden sucesivo las fotos de los objetos de antes de ser restaurados y una vez ya restaurados, para esta labor se ha tardado 14 años desde 2018-2021.
— Espero que os haya gustado y nos vemos en próximas publicaciones, que pasen una buena semana. - ようこそ、ジャポニスタサルケオロジコスの日本考古学の新しい回へ、この機会に私はあなたに、とりわけ、雄牛のサイトから回収されたいくつかのオブジェクトを表示します。 - 可動遺物:木や骨で作られたもので、今回のように最適な条件でない限り、保存されることはほとんどない。2018年から2021年までの14年間を費やしたこの作業のために、修復される前と、すでに修復されたものの写真を順を追って並べます。
- お気に召していただけたなら幸いである。 - Welcome japonistasarqueologicos, to a new installment of Japanese archaeology, on this occasion I will show you some objects recovered from the site of the bull, among others - Movable goods: these are all those materials made of wood and bone that are rarely preserved, unless the conditions are optimal as in this case. I will put in a successive order the photos of the objects before being restored and once already restored, for this work it has taken 14 years from 2018-2021.
- I hope you liked it and see you in future publications, have a good week.
More information: https://www.shizuoka-toromuseum.jp/zhcn/
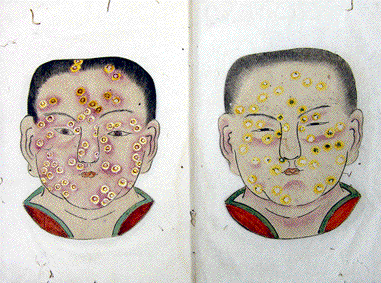
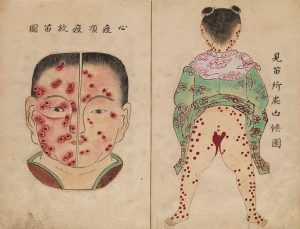
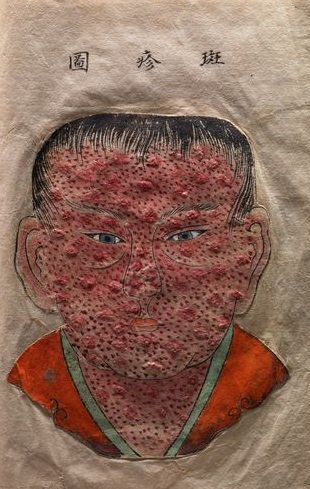


Sean bienvenidos a una nueva entrega de historia en esta ocasión, os comentaré una de las epidemias que azotó al país del Sol naciente una vez dicho esto póngase cómodos que empezamos. - La epidemia tuvo lugar en el periodo Nara (710-794) y la espidemia tubo lugar en 735-737.¿Conocían la epidemia? - Espero que os guste y nos vemos en próximas publicaciones, que pasen una buena semana. - Welcome to a new installment of history on this occasion, I will tell you about one of the epidemics that hit the country of the rising sun, having said that, make yourself comfortable and let's start. - The epidemic took place in the Nara period (710-794) and the epidemic took place in 735-737. Did they know about the epidemic? - I hope you like it and see you in future publications, have a good week. - この機会に、新たな歴史へようこそ。日出ずる国を襲った疫病の一つについてお話します。そうは言っても、気を楽にして始めましょう。 - 奈良時代(710年~794年)に流行し、735年~737年に流行しました。 彼らは疫病について知っていましたか? - 気に入っていただければ幸いです。今後の出版物でお会いできることを願っています。良い一週間をお過ごしください。


Sean bienvenidos, japonistasarqueológicos a una nueva entrega, de arqueología en la que comentaremos, cómo era vivir hace 2000 años en el período Yayoi, una vez dicho esto pónganse cómodos que empezamos. — En el emplazamiento, podréis vivir la experiencia de como si estuvierais en las viviendas, de dicho periodo, las recreaciones de los almacenes y los santuarios de las ruinas de toro se han reducido a una escala de aproximada al 80 % las paredes representan la naturaleza, de la época y de su estilo de vida. Siéntete como si hubieras viajado en el tiempo al pueblo Toro del período Yayoi, con nuestra máquina del tiempo, ya que puede ser una experiencia inolvidable, para todas las edades, porque la vida no ha cambiado en 2000 a 3000 años. — Espero que os guste y nos vemos en próximas publicaciones, que pasen una buena semana.
-
日本の考古学者諸君、ようこそ考古学の新連載へ。2000年前の弥生時代の暮らしとはどんなものだったのかについて語り合おう。 - 遺跡では、当時の住居がどのようなものであったかを体験することができます。トロ遺跡の倉庫や神社を約80%の縮尺で再現し、壁で当時の自然や生活様式を表現しています。まるでタイムマシンで弥生時代の登呂集落にタイムスリップしたかのような体験は、2000年から3000年経っても変わらない暮らしの中で、世代を問わず忘れられない思い出になることだろう。 - それでは、また次回もお楽しみに。
-
Welcome, Japanese archaeologists, to a new instalment of archaeology in which we will discuss what it was like to live 2000 years ago in the Yayoi period, so make yourselves comfortable and let's get started. - At the site, you can experience what it was like to live in the dwellings of that period, the recreations of the warehouses and shrines of the toro ruins have been reduced to a scale of about 80% and the walls represent the nature of the period and its lifestyle. Feel as if you have travelled back in time to the Toro village of the Yayoi period, with our time machine, as it can be an unforgettable experience, for all ages, because life has not changed in 2000 to 3000 years. - I hope you like it and see you in future publications, have a nice week.
詳しくは/more information:
https://www.shizuoka-toromuseum.jp/guide/admission/




Introducción a la cerámica Jōmon: - Tipos cerámica Jōmon se dividen en 5 : 1 fukabachi 2 hachi 3 asabachi 4 tsubo 5 chuko - ¿Cónocian algúnos de estos tipos? os deseo un feliz día un cordial saludo. - Introduction to Jōmon Pottery: - Jōmon ceramic types are divided into 5: 1 fukabachi 2 hachi 3 asabachi 4 tsubo 5 chuko - Do you know any of these guys? I wish you a happy day, a cordial greeting. - 縄文土器の紹介: - 縄文土器は次の5種類に分類されます。 深鉢 1個 2ハチ 3アサバチ 4坪 5中子 - この人たちを知っている人はいますか? 幸せな 一日をお祈りします。心からのご挨拶を申し上げます。